The growth stories of frontier economies


Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Economic Progress
The growth story for frontier economies isn’t the same as China’s in the last two decades, or the United States a hundred years ago. These fast growing, low-income countries have their own story, and it’s not what you might think.
In May of this year, I wrote about who they are and how they are different, and now I want to go into a bit more detail about how their economies have been on the rise and how they have moved themselves to the frontier.
Not your grandfather’s growth story
Although the countries’ economic paths vary like snowflakes— no two are the same—their growth stories have two distinct features.
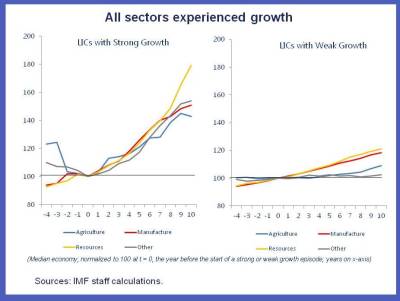
First, frontier economies like Bangladesh, Tanzania, and Mozambique, to name just a few, have a different growth story from the United States or China because they are not growing by moving their economy from agriculture, to manufacturing, then to services: they are growing across all of them, as you can see in this chart:
Second, despite this different growth path, frontier economies have made progress when you compare their economic size relative to an advanced economy like the United States—a process known as convergence.
This is due in large part to more stable and predictable fiscal and monetary policies, strong investment and exports, better debt management, less red tape, stronger institutions, strong productivity gains, and access to capital markets.
The next chapter
Looking ahead, a number of factors will help these economies continue to achieve strong growth. They will reap the benefits of a large, young, working-age population for years to come. They are well endowed with natural resources. They are making inroads in global ties. They have a growing middle class, which creates potential for new markets.
All well and good, you’re thinking, but weak global demand, tumbling oil prices and the expected end to the unconventional monetary policies in the United States could pose risks for frontier economies. All true.
Indeed, many frontier economies are established or prospective commodity exporters and have benefited from high commodity prices. A sharp decline in commodity prices could adversely affect export earnings, derail investment programs, and raise the risks associated with foreign borrowing.
Also, the recent surge in sovereign bond issuances by frontier economies could leave the latter vulnerable to roll over risks when the bonds mature, particularly given their large size relative to the countries’ reserve and other foreign assets.
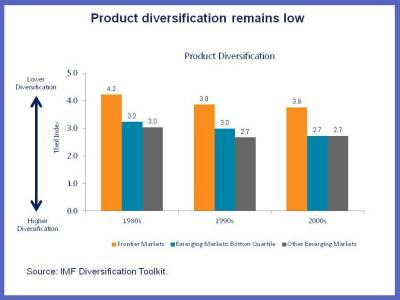
We see two additional vulnerable spots to keep an eye on. Frontier economies have historically depended on a narrow range of primary products for export to make money, so they need to diversify to make themselves less vulnerable to the whims of the rest of the world, including commodity price movements. This chart shows their progress on this issue over the last few decades:
They also need to increase the quality of what they produce and move up that proverbial ladder because faster growth in quality is associated with higher per capita incomes and higher economic stability. Opportunities for countries to upgrade the quality of their products are strongest in manufacturing but also exist in agriculture. This is particularly important because a large portion of the population in these countries is often employed in the agricultural sector.
Chance favors the well prepared
At this point the question is how will frontier economies prepare for what happens next?
First, they need to continue to implement appropriate monetary and fiscal policies to maintain stability and weather what lies ahead. Economic stability is particularly important to manage risks associated with foreign borrowing.
Second, they need to implement the difficult next generation of reforms, such as improvements in public finance management, while they move away from policies that can exacerbate a downturn, such as cutting back on spending. They should also deepen the linkages between their economic sectors, such as agriculture and manufacturing.
Continued efforts to improve public finance management will also help ensure that public investments are efficient and balanced against debt sustainability risks. Also, they will help improve the quality of products across all sectors as well as their exports.
This article is published in collaboration with IMF Direct. Publication does not imply endorsement of views by the World Economic Forum.
To keep up with Forum:Agenda subscribe to our weekly newsletter.
Author: Min Zhu assumed the position of Deputy Managing Director of IMF on July 26, 2011.
Image: A Zimbabwean trader sells fruit and vegetables at a rural marketplace in Domboshava outside the capital Harare, April 5, 2008. REUTERS/Mike Hutchings.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Economic GrowthSee all
Emma Charlton
April 24, 2024
Piyachart "Arm" Isarabhakdee
April 23, 2024
Pooja Chhabria and Kate Whiting
April 23, 2024
Pedro Conceição
April 22, 2024
Joe Myers
April 19, 2024
Joe Myers
April 12, 2024