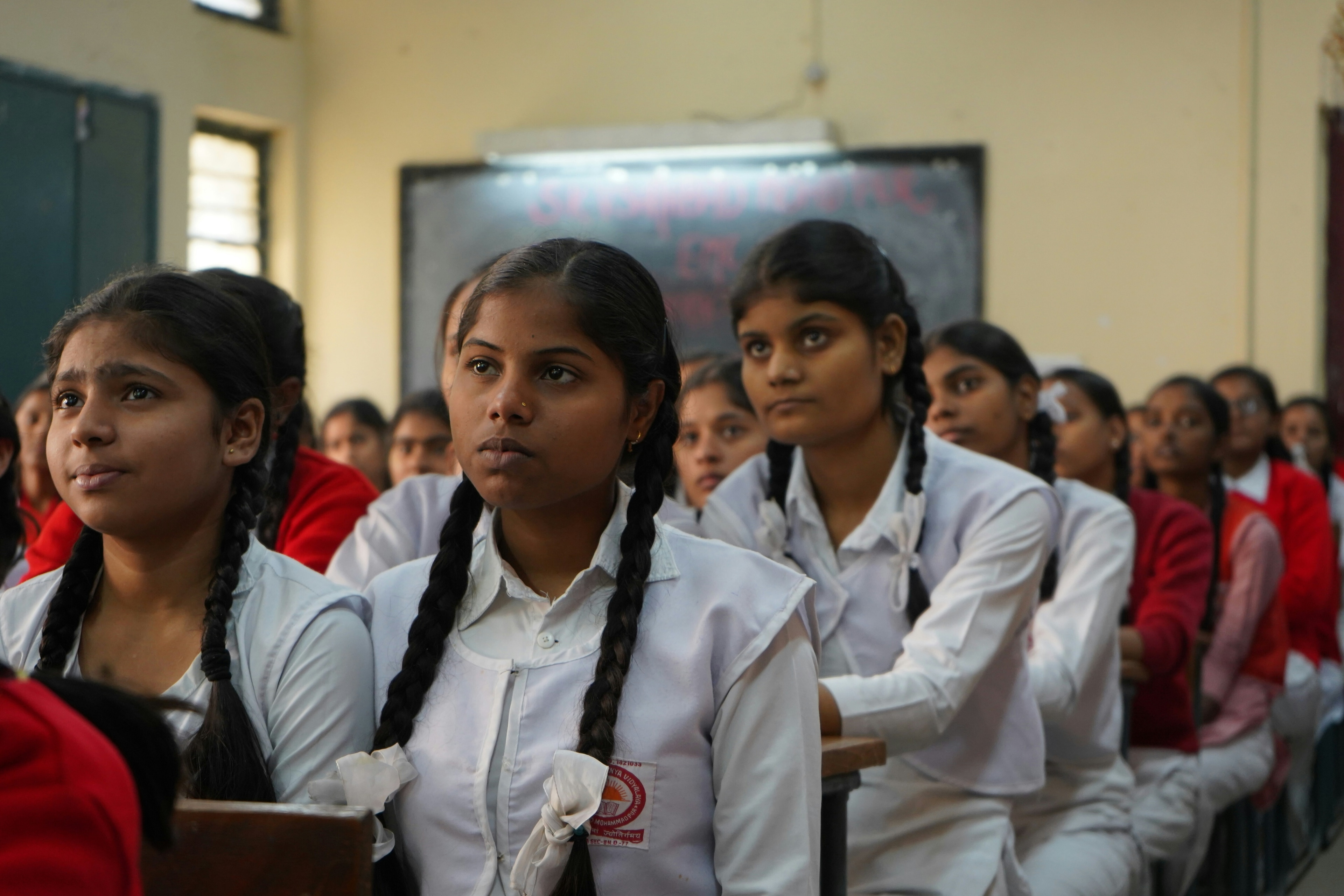
Is technology destroying more jobs than it creates?


Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Artificial Intelligence
The technology is here. But the jobs are nowhere to be found.
Thanks to the efficiency of the internet and automated systems, productivity and GDP have grown during the last few decades, but the middle class and jobs are disappearing.
In fact, we have reached a tipping point where technology is now destroying more jobs than it creates. And if the trend continues we could face a serious crisis in the US and abroad, said Wendell Wallach, a consultant, ethicist, and scholar at the Yale University Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics.
Robots, 3D printing, and other emerging technologies are all fueling technological unemployment and global wealth disparity, Wallach said.
Technological unemployment is the concept of technology killing more jobs than it produces. While that fear has been considered a Luddite fallacy for the past 200 years, it is now becoming a stark reality, he said.
“This is an unparalleled situation and one that I think could actually lead to all sorts of disruptions once the public starts to catch on that we are truly in the midst of technological unemployment,” Wallach said during a presentation at the Carnegie Council for Ethics and International Affairs on Tuesday.
And yet there are no signs of the trend reversing. Because technology is evolving faster than ever before with little to no oversight or regulation, the likelihood of more jobs being replaced by new tech is at an all-time high, Wallach told Business Insider.
In fact, some 47% of present jobs in the US could be computerized in the next 10 to 20 years, according to an Oxford University study published in 2013.
Wallach, who authored “A Dangerous Master: How to Keep Technology from Slipping Beyond Our Control,” said that as new technologies continue to displace workers, wage stagnation in the US and around the world will also continue to grow.
Traditionally, elements like productivity, jobs, hourly wages, and income all grew in unison. However, during the last 30 years GDP and productivity grew while the US median income stopped and employment flattened, Wallach writes in his new book. Technology innovation has played a significant role in this trend.
“For most of our history 50% of GDP went to wages and 50% went to capital, and we are seeing a radical alteration in that largely because of the anomalies of money being made in high tech industries,” he said. “That’s not anybody doing anything wrong, that’s just technology industries are different from old manufacturers.”
So, for example, in 1990 GM, Ford, and Chrysler brought in $36 billion in revenue and hired over a million workers, Wallach said. The big three today — Apple, Facebook, and Google — bring in over a trillion dollars in revenue and only have about 137,000 workers, he said.
This change has created a situation where more and more of the capital is going to a smaller percentage of the population. In fact, we are on course for 70% of stock ownership to be held by 5% of the population, Wallach said.
This is a dangerous scenario because it could potentially lead to massive social unrest, possibly even revolutions.
“When people no longer receive the money from wages they need to support their families, it is hard to know what they will do, but in the past and in other countries this has been thought of as a situation ripe for a revolution,” Wallach said.
However, he added, that such a crisis could be averted if government take action to fix wealth distribution.
“That kind of dire response can of course be avoided through welfare reforms or job subsidies, but these would require redistributing some of the capital growth achieved through from increased productivity,” he said.
This article is published in collaboration with Business Insider. Publication does not imply endorsement of views by the World Economic Forum.
To keep up with the Agenda subscribe to our weekly newsletter.
Author: Cadie Thompson is the emerging tech editor at Business Insider.
Image: Twendy-One, a robot designed to help elderly and disabled people around the house, demonstrates serving toast at Waseda University in Tokyo. REUTERS/Issei Kato.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Artificial IntelligenceSee all
TeachAI Steering Committee
April 16, 2024
Darko Matovski
April 11, 2024
Juliana Guaqueta Ospina
April 11, 2024
Allan Millington
April 10, 2024