Will the future be gender equal?

Mind the gap ... at current rates, women won't achieve equal pay until 2133 Image: REUTERS/Daniel Munoz

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Gender Inequality
Achieving gender equality isn't just a moral issue – it makes economic sense. Equality between men and women in all aspects of life, from access to health and education to political power and earning potential, is fundamental to whether and how societies thrive.
The most important factor in a country’s competitiveness is its human talent – the skills and productivity of its workforce. It is the same for a company or an organization. That’s why the proper participation of half the world’s population is so important for the well-being of both businesses and countries.
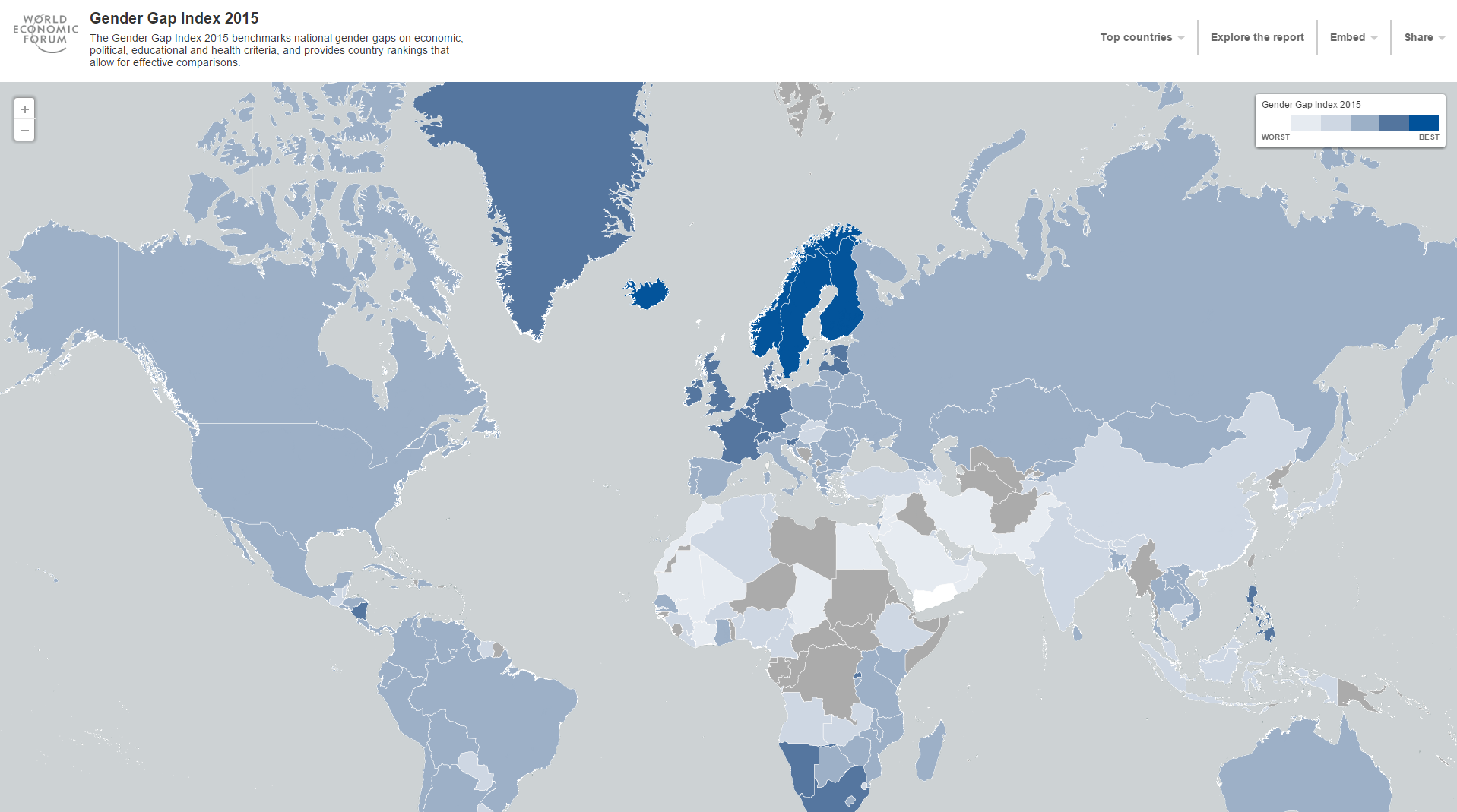
What’s the problem?
Although we are getting closer to gender parity, change isn't happening fast enough. For the past decade, we've been measuring the pace of change through our Global Gender Gap Report, and at current rates, it would take the world another 118 years – or until 2133 – to close the economic gap entirely.
In the 10 years the Forum has been reporting on the gap between men and women in health, education, economic opportunity and political representation, the gap has only narrowed by 4% overall.
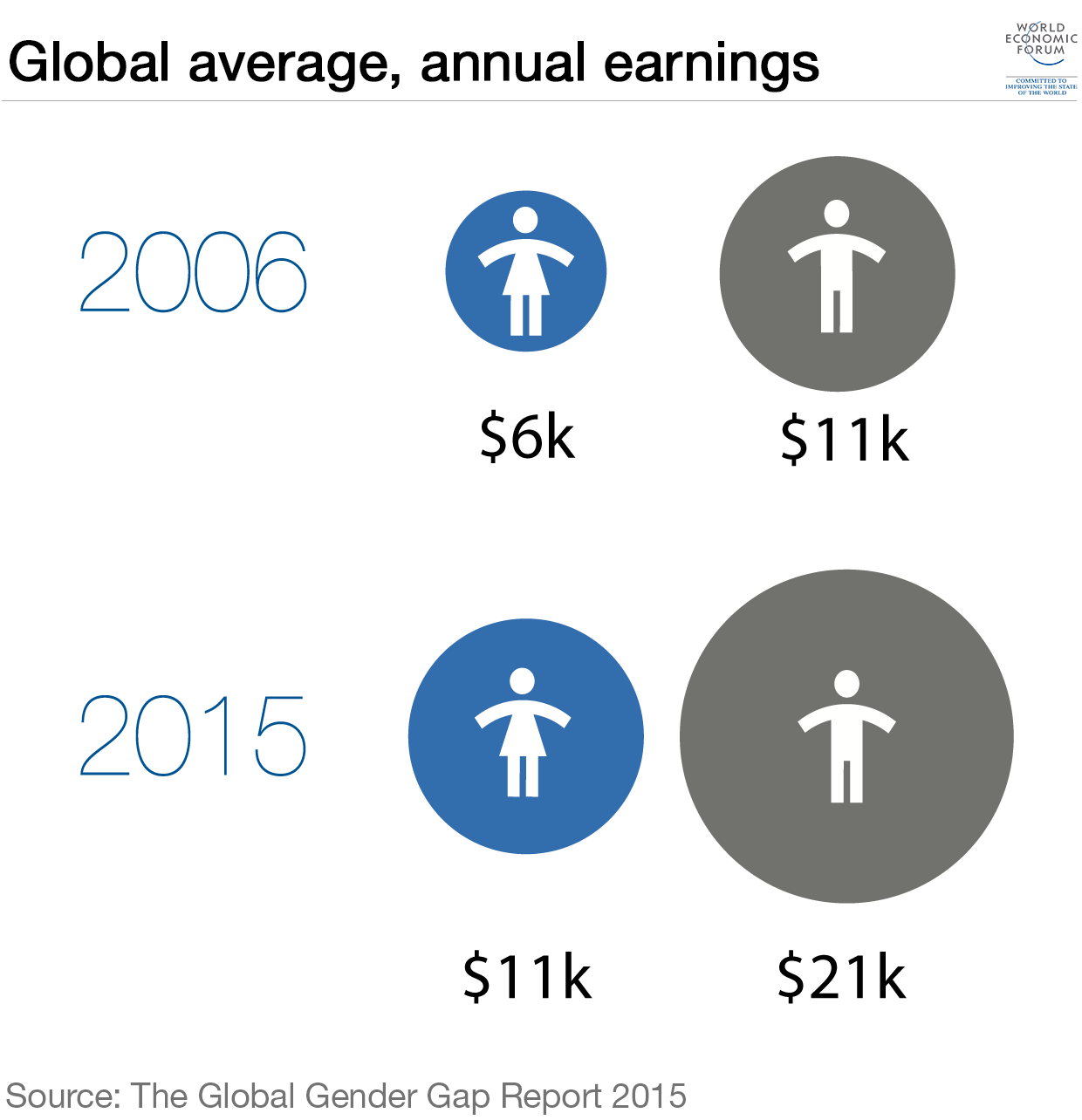
Progress towards wage equality has stalled in the wake of the global financial crisis. This means that although an additional quarter of a billion women have entered the workforce, women are only now earning the amount men did in 2006.
Is education the main issue?
It is becoming apparent that reducing the gap between men and women in education does not automatically lead to a closing of the economic divide.
More women than men are now enrolled in university in the majority of countries covered by the Global Gender Gap Report, but men still outnumber women in skilled jobs.
Only four countries in the world – Philippines, Colombia, Fiji and Ghana – have more women than men in senior roles in the workplace.
So how do you increase women’s economic and political power?
The Forum’s work indicates that there is a strong correlation between economic and political empowerment. The two appear to reinforce each other.
As women get ahead at work they seek better representation in politics. Female politicians serve as role models and support policies that help people balancing formal work and informal care roles.
It is clear that achieving gender parity requires an understanding of a very complex interplay of factors that affect rights and opportunities for women.
Are we on the right track?
There has been a significant increase in awareness of the importance of gender parity and much has been done by international organizations, civil society, governments and business.
However, often the work centres on single-issue awareness-raising campaigns. Existing work also frequently involves either cooperation between different public bodies or different private bodies. More needs to be done to bridge the gap and facilitate cooperation between the public and private sectors.
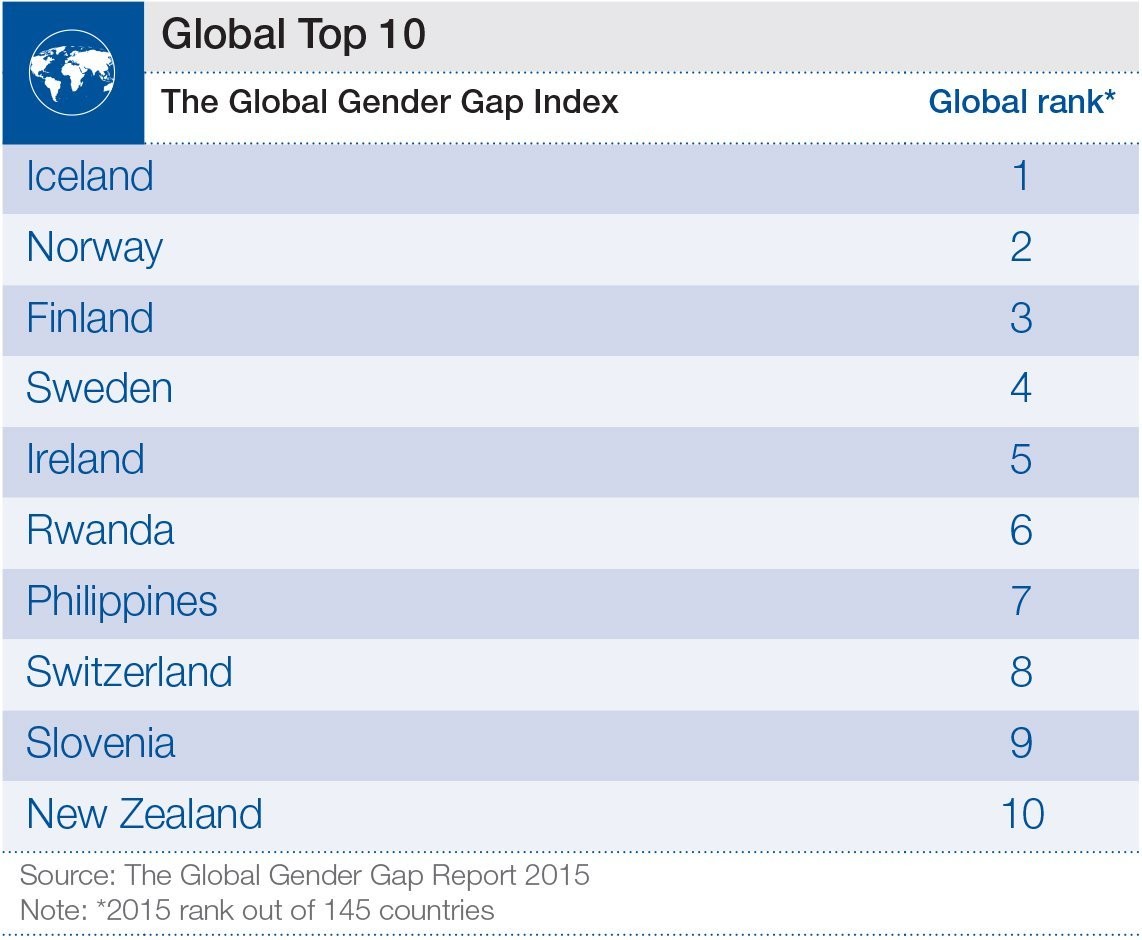
What is the World Economic Forum doing about it?
The Forum's Global Gender Gap Report has done a great deal to highlight this issue and serves as a tool for measuring progress.
The Forum has many other initiatives in this area. It is carrying out an analysis of specific industries and using this to put together a set of best practices so that successful policies can be shared. It has also been working with countries to set up national gender parity taskforces, which bring together government and industry leaders to devise programmes and policies to close the gender gap.
Finally, we've carried out a survey on the future of jobs with a dedicated gender dimension to understand how expected changes in industry will affect women. The survey has looked at a wide range of industries with a view to identifying the challenges and opportunities the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring.
This ground-breaking report, which will be published in Davos this month, will help shape the direction of national and international policies in this area in the years to come.
Click here for more information on the Forum's Global Challenge on Gender Parity.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Gender InequalitySee all
Morgan Camp
April 9, 2024
Rida Tahir
April 9, 2024
Andrea Willige
April 8, 2024
Gilles Roucolle and Sumati Sharma
April 5, 2024
Victoria Masterson
April 5, 2024






