These 5 simple habits could add years to your life

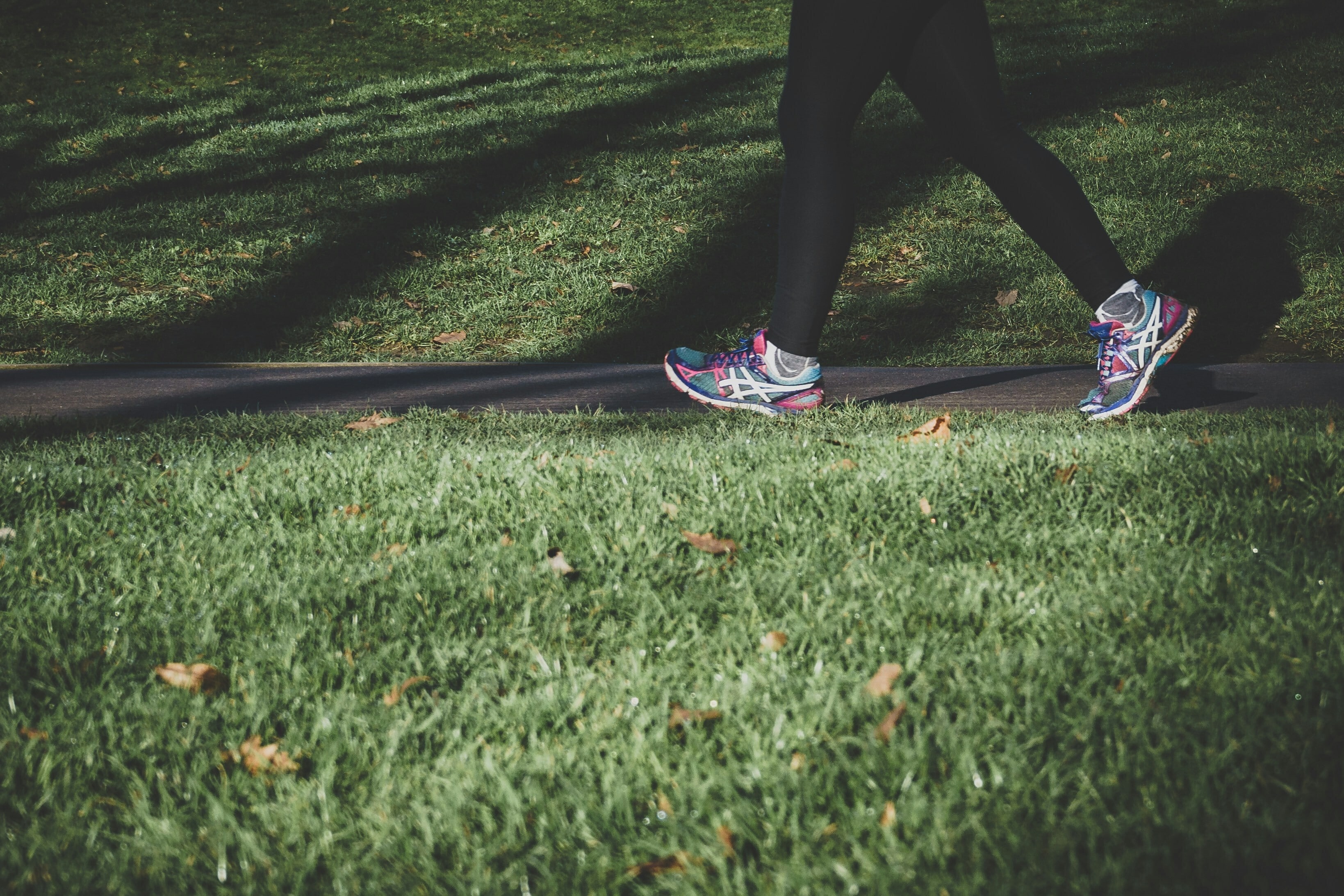
A group of key healthy lifestyle habits can have a dramatic effect on mortality rates. Image: REUTERS/Kim Kyung-Hoon

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Health and Healthcare
Lifestyle habits in adulthood may increase women’s life expectancy by 14 years, men gain 12
Maintaining five healthy habits — eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, keeping a healthy body weight, not drinking too much alcohol, and not smoking — during adulthood may add more than a decade to life expectancy, according to a new study led by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Researchers also found that American women and men who maintained the healthiest lifestyles were 82 percent less likely to die from cardiovascular disease and 65 percent less likely to die from cancer when compared with those with the least healthy lifestyles over the course of the roughly 30-year study period.
The study is the first comprehensive analysis of the impact that adopting low-risk lifestyle factors has on life expectancy in the U.S. It will be published online today in Circulation.
Americans have a shorter average life expectancy — 79.3 years — than almost all other high-income countries. The U.S. ranked 31st in the world for life expectancy in 2015. The new study aimed to quantify how much healthy lifestyle factors might be able to boost longevity in the U.S.
Harvard Chan researchers and colleagues looked at 34 years of data from 78,865 women and 27 years of data from 44,354 men participating in, respectively, the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. The researchers looked at how five low-risk lifestyle factors — not smoking, low body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), at least 30 minutes or more per day of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (for example, up to about one 5-ounce glass of wine per day for women, or up to two glasses for men), and a healthy diet — might impact mortality.
For study participants who didn’t adopt any of the low-risk habits, the researchers estimated that life expectancy at age 50 was 29 years for women and 25.5 years for men. But for those who adopted all five, life expectancy at age 50 was projected to be 43.1 years for women and 37.6 years for men. In other words, women who maintained all five healthy habits gained, on average, 14 years of life, and men who did so gained 12 years, compared with those who didn’t maintain healthy habits.
Compared with those who didn’t follow any of the healthy lifestyle habits, those who followed all five were 74 percent less likely to die during the study period. The researchers also found that there was a dose-response relationship between each individual healthy lifestyle behavior and a reduced risk of early death, and that the combination of all five healthy behaviors was linked to the most additional years of life.
“This study underscores the importance of following healthy lifestyle habits for improving longevity in the U.S. population,” said Frank Hu, chair of the Department of Nutrition at Harvard Chan School and senior author of the study. “However, adherence to healthy lifestyle habits is very low. Therefore, public policies should put more emphasis on creating healthy food, built, and social environments to support and promote healthy diet and lifestyles.”
Other Harvard Chan School study authors included Yanping Li, Dong Wang, Xiaoran Liu, Klodian Dhana, Meir Stampfer, and Walter Willett.
Funding for the study came from grants UM1 CA186107, R01 HL034594, R01 HL60712, R01 HL088521, P01 CA87969, UM1 CA167552, and R01 HL35464 from the National Institutes of Health.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Health and HealthcareSee all
Johnny Wood
April 17, 2024
Adrian Gore
April 15, 2024
Carel du Marchie Sarvaas
April 11, 2024
Nancy Ip
April 10, 2024
Shyam Bishen
April 10, 2024