Here’s how vulnerable to automation your job is

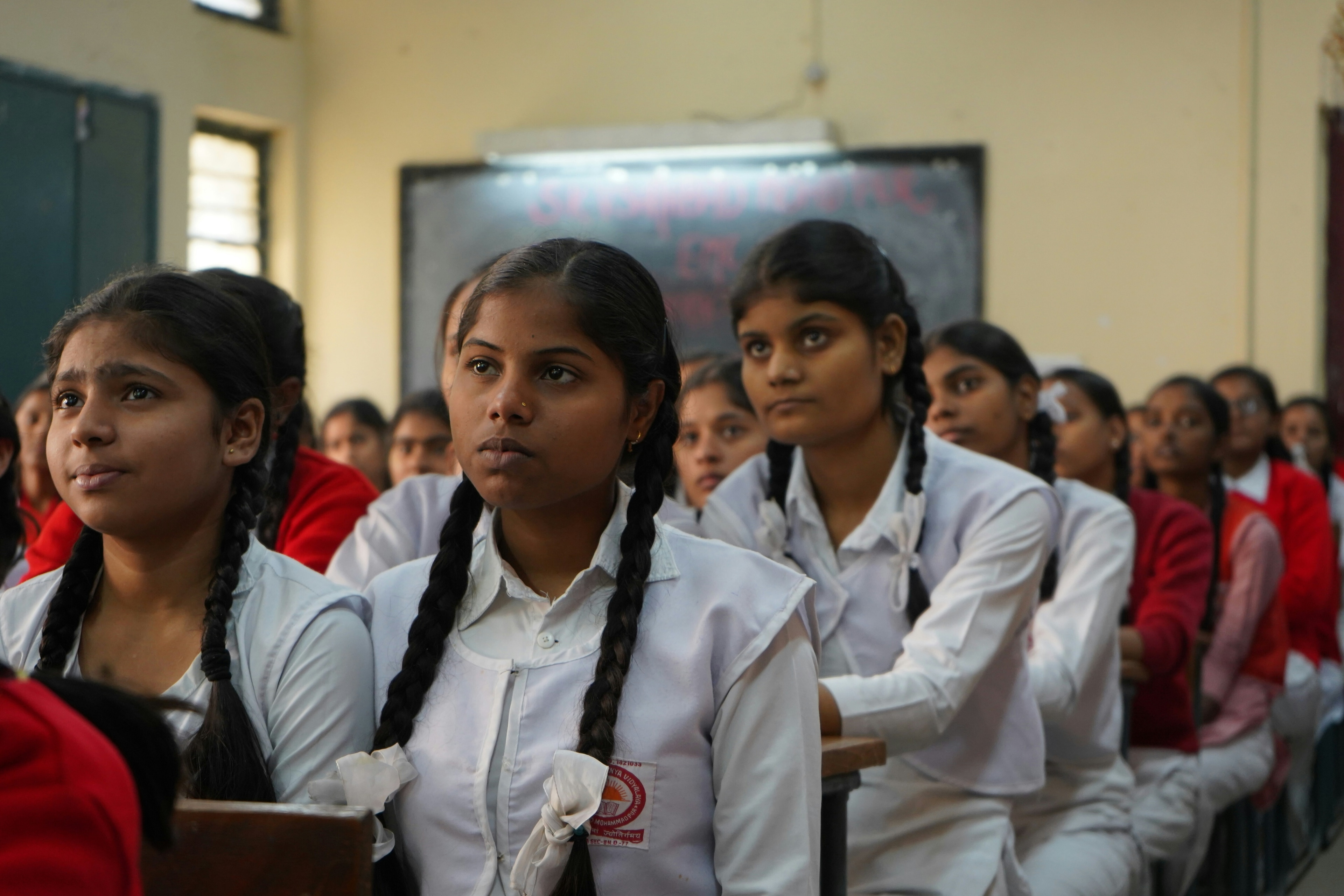
What impact will the robot revolution have? Image: REUTERS/Darrin Zammit Lupi

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Artificial Intelligence
Another week, another warning about technology taking your job.
This time it comes in the shape of a report from the OECD that finds “the tasks that AI and robots cannot do are shrinking rapidly.” The report goes on to say 14% of jobs across 32 countries are “highly vulnerable” to automation.
Such themes are not new. A World Economic Forum report on jobs predicted the Fourth Industrial Revolution would transform labour markets and the Bank of England’s Chief Economist, Andy Haldane, has warned "large swathes" of people could become "technologically unemployed."
The OECD’s report says that in addition to the highly vulnerable roles, a further 32% of jobs will see significant changes to the way they are carried out.
This chimes with other research suggesting the effect of automation is unlikely to be felt equally. A PwC report on U.K. jobs identified the likely “winners” and “losers” by industry sector. It said health, scientific and technical services and education would see an increase, while manufacturing, transport and public administration would see the largest losses.
Still, in the U.K., the net gain was likely to be “broadly neutral,” it concluded, with around the same number of jobs being created as are displaced. That report suggested education holds the key and said the government should invest more in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, as well as art and design, to foster innovation. It also recommended “strengthening the safety net” for those who may find it hard to adjust to the technological changes.

“People are understandably worried about the impact of AI on jobs, and businesses and the government need to address these concerns head on,” said Euan Cameron, U.K. AI leader at PwC. “It’s likely that the fourth industrial revolution will favour those with strong digital skills, as well as capabilities like creativity and teamwork which machines find it harder to replicate.”
The training gap
Job-related training will need to be a central part of the response to automation, but there are wide variations in training provision from country to country For example, 16% of workers participated in job related training in Greece and Turkey, compared with 60% in New Zealand and Denmark.

The OECD’s report calls for policies to educate workers to deal with the changes that are likely to occur. As well as skills like cognitive and social intelligence it also advocates more digital training. The findings are in line with the Forum’s Future of Jobs report, which identified the skills needed to keep pace with rapid advances in technology.

In his predictions, Andy Haldane suggested jobs that focus on skills of human interaction, face-to-face conversation and negotiation would be likely to flourish, while manual jobs are more at risk. The Forum’s report identified how the skills needed are evolving, with creativity leapfrogging to become the third most important skill by 2020, up from 10th on the list in 2015.
“So far, the debate on these transformations has been sharply polarized between those who foresee limitless new opportunities and those that foresee a massive dislocation of jobs,” the Forum report said. “In fact, the reality is likely to be highly specific to the industry, region and occupation in question and the ability of various stakeholders to successfully manage change.”
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Artificial IntelligenceSee all
TeachAI Steering Committee
April 16, 2024
Darko Matovski
April 11, 2024
Juliana Guaqueta Ospina
April 11, 2024
Allan Millington
April 10, 2024