Struggling to focus at work? Air pollution could be to blame

The data study indicates that air pollution damaged cognitive function in working-age adults Image: Unsplash/ Maxim Tolchinskiy

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Global Health
- PM2.5 are tiny particles 2.5 microns or less in size.
- If inhaled, PM2.5 can penetrate the lungs, enter the bloodstream, and cause serious health problems.
- A new study shows that the effects of air pollution are largest for those under 50, with the most damaging effects being memory.
Researchers have found that even short-term exposure to air pollution affects our brain performance and capacity to work.
The data study indicates that air pollution damaged cognitive function in working-age adults, says Andrea La Nauze from the University of Queensland’s School of Economics.
“Our research used data from Lumosity brain training games to investigate the impact of air pollution on adults living in the United States,” La Nauze says.
“The games we studied targeted seven cognitive functions: memory, verbal ability, attention, flexibility, maths ability, speed, and problem-solving.
“We found that exposure to moderately high levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) caused a player to drop by almost six points in a 100-point scale where 100 represents the score of the top 1% of cognitive performers.
“In fact, if you’re under 30 years old and you’re exposed to this level of pollution, your cognitive function declines by the same amount as aging by 15 years.”
PM2.5 are tiny particles 2.5 microns or less in size. If inhaled, PM2.5 can penetrate the lungs, enter the bloodstream, and cause serious health problems, including heart disease and respiratory issues.
La Nauze says while the health effects of PM2.5 were widely understood, this research was the first to use brain training data to study the potential impact on cognitive performance.
“Cognitive functions are skills that we use to process, store, and use information—they’re critical to tasks ranging from making a cup of tea to self-regulating,” she says.
“Economists are just beginning to study cognition, but recent research suggests changes in cognitive function impact workforce productivity.
“Our results show the effects of air pollution are largest for those under 50—people of prime working age—which indicates that day-to-day performance in our jobs is also likely to be impacted.”
The study found the largest effects were on memory, meaning occupations that rely more on memory function are likely to be most affected.
Although the study used United States data, La Nauze says the results are relevant to Australia.
“We believe our research has real implications for the average working-age Australian adult, particularly as bushfires become more frequent and contribute to air pollution levels,” she says. “The 2019-2020 bushfire crisis subjected millions of Australians to the worst air pollution in the world.
“Although Australia’s air is pretty clean by international standards, the average Australian is still exposed to higher levels of air pollution than the latest World Health Organization recommendations.”
La Nauze says a combination of individual and policy measures could combat the effects.
“You can alter your exposure in small ways by staying indoors, using air filtration, or moving to a less-polluted suburb,” she says.
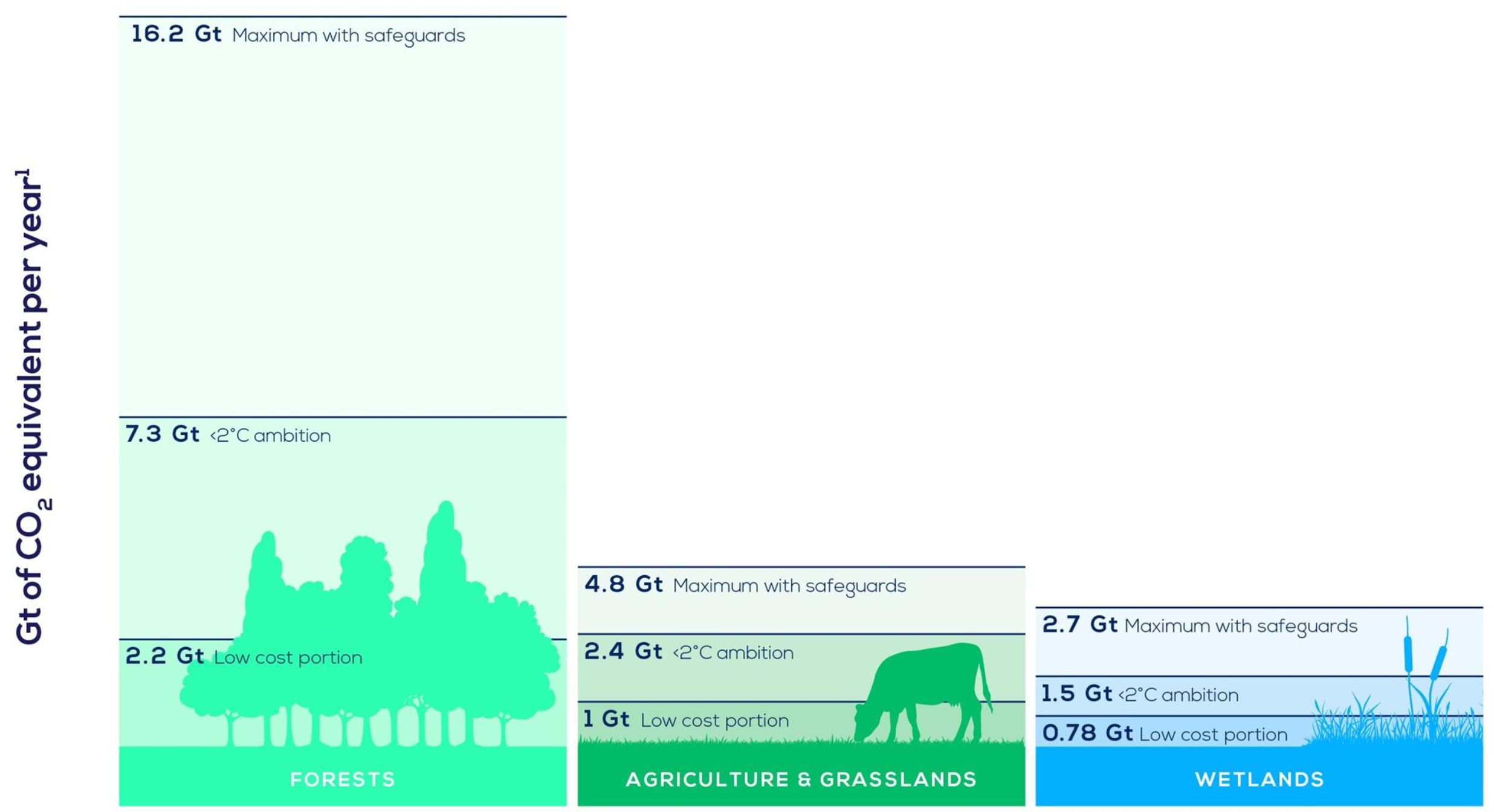
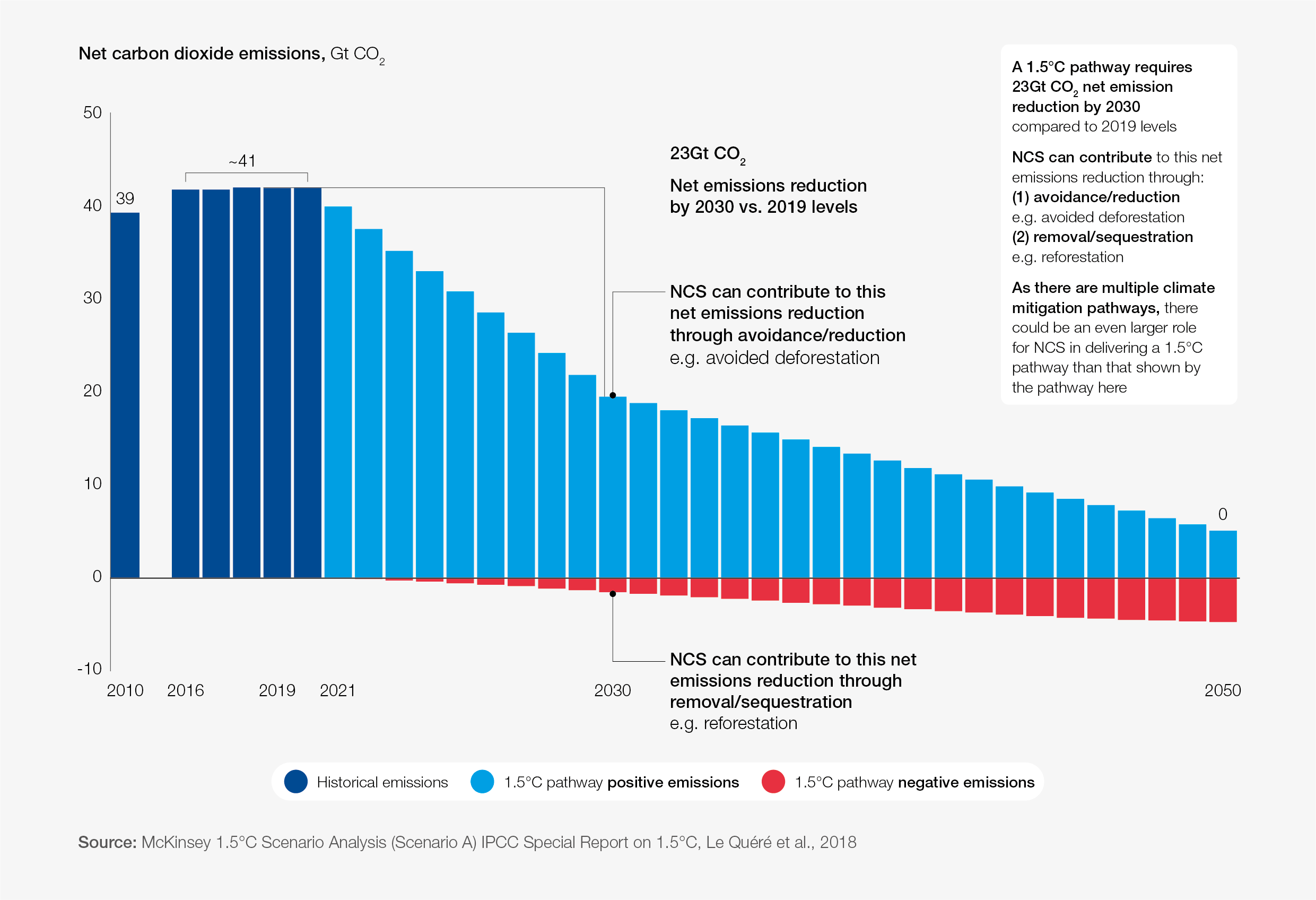
What is the World Economic Forum doing on natural climate solutions?
“Fundamentally though, it comes down to government policy: reducing vehicle emissions, targeting sources of air pollution such as bushfires, and revising air-quality standards.
“Air-quality standards in Australia and around the world should take into account the cognitive effects and their downstream productivity impacts.”
The study appears in the National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper series. Additional researchers from Carnegie Mellon University contributed to the work.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Wellbeing and Mental HealthSee all
Kate Whiting
April 17, 2024
Adrian Gore
April 15, 2024
Fatemeh Aminpour, Ilan Katz and Jennifer Skattebol
April 15, 2024
Andrew Moose and Ruma Bhargava
April 5, 2024
Jacqueline Brassey, Lars Hartenstein, Patrick Simon and Barbara Jeffery
April 3, 2024