Why COVID-19 shows the future not the end of globalization

During the COVID-19 pandemic, societies have managed to maintain normal life because goods have been delivered to our doorstep Image: REUTERS/Edgar Su
- The COVID-19 pandemic shows us that global connectedness is not a problem, but a solution that can benefit us all;
- Despite the pandemic, globalization has proved far more robust than expected. The DHL Global Connectedness Index 2020 suggests the world’s level of global connectedness this year is unlikely to fall below levels seen during the 2008-09 global financial crisis;
- As communities and business sectors recover, the logistics industry needs to articulate the value of trade and globalization in fighting this and future crises.
“Wave goodbye to the greatest era of globalization — and worry about what is going to take its place,” wrote The Economist in May.
I’ve long been a strong advocate of globalization but, in 2020, even my own convictions have been momentarily challenged. A virus that knows no borders has “pecked away” at the foundations of the way we live and the way we trade.
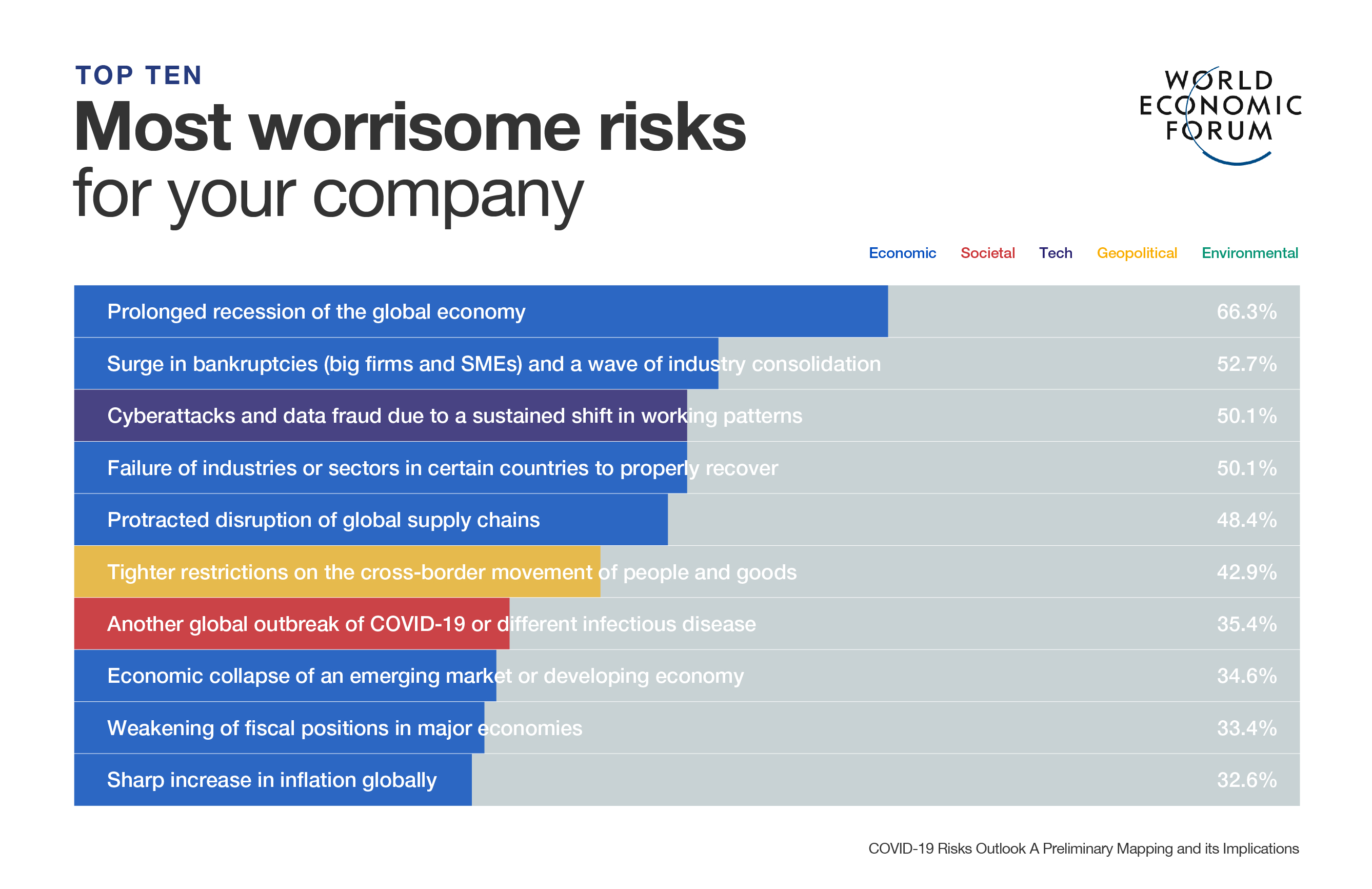
How long will governments keep borders sealed? Will these physical borders evolve into trade borders and will more governments try to keep the outputs of trade within their own borders? Shortages in vital provisions – such as personal protective equipment and ventilators – have precipitated calls for change. We’ve heard voices demanding a return to domestic manufacturing and the renationalization of critical industries. We have heard it all.
The idea that firms and their products should be treated equally regardless of where they come from is in peril. If these and other thoughts proliferate, trade will cease to flow freely. Countries will become less connected and the cornerstones of the commercial world we’ve become accustomed to will begin to creak and crack.
Is this the end of globalization as we know it?
Opportunities in disguise
I, for one, am not convinced. This pandemic has shown us that global connectedness is in fact not the problem, but the solution.
It is simply amazing how quickly the world has adapted to a new way of being. To a large extent, societies have managed to maintain normal life because goods have been delivered to our doorstep. We’ve kept in touch with friends, family and work through digital connections.
Thanks to global collaboration, we’re getting closer to finding effective treatments and vaccines for this virus. Adaptable supply chains and access to the global market are helping us soften the economic impact.
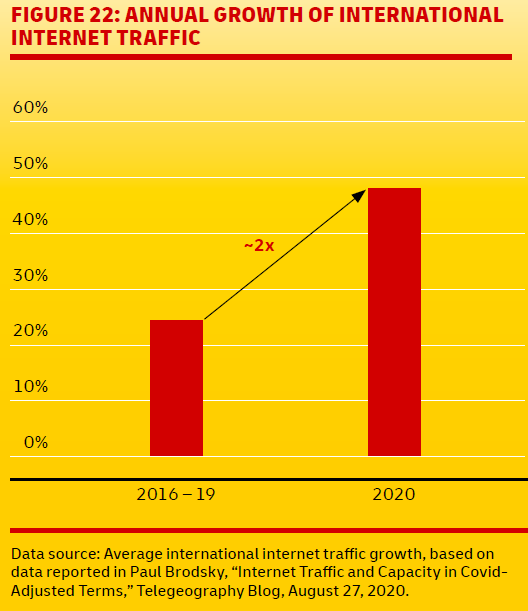
The benefits of a connected world are visible everywhere. We’ve witnessed huge growth in cross-border e-commerce. Many companies with a global reach have found themselves in a much better position during this crisis than those with a purely national or regional focus.
DHL Global Connectedness Index: encouraging signals
The truth is globalization has proved far more robust than expected. The newly released DHL Global Connectedness Index 2020, published in partnership with New York University’s Stern School of Business, bears this out.
After holding steady in 2019, the world’s level of global connectedness is set to decline in 2020 owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, but it is unlikely to fall below levels seen during the 2008-09 global financial crisis. Given the scale of the pandemic that surprising resilience is something in itself.
While lockdowns and border closures have sharply diminished global mobility, the new report shows that capital flows have already started to recover; trade has rebounded strongly and digital information flows have surged.
We’ve still been able to buy food and clothes and improve our homes and gardens. Entertainment services such as Netflix and Amazon have flourished and we have stayed in touch through Skype, Facetime and Zoom.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a setback for travel, tourism and other flows, but this is not new. The September 11 attacks in 2001, the SARS virus of 2002, the global financial crisis of 2008, the ash cloud event of 2010 and the US-China trade war all interrupted and stalled global exchange, but it always recovered. It seems business heals when it comes to global trade.
The way we’ve all adapted in 2020 has been astonishing. Logistics companies like our own have played a vital role in keeping the world running through this crisis. When economies all but closed down, our industry remained operational, literally oiling the wheels of trade.
When lockdowns grounded commercial flights, our specialists redesigned our network in just a few weeks; when borders were closed, our road transport experts found new routes; and when companies swung back into action after forced plant closures, we made sure that they were stocked, machinery could restart and production could continue.
Logistics will continue to play a crucial role in helping the world mitigate this crisis. Who is going to manage the effective distribution of vaccines when they arrive? To get billions of doses of COVID-19 vaccine to people around the world will require many thousands of flights and cooling boxes. It will require local warehousing capacity and know-how of in-country logistics. It will require all of this and more – in big doses.
Harnessing the power of ecommerce
Logistics help to provide essential continuity, but this crisis has hit many areas hard. Sport, live entertainment and education have endured massive disruption, but the outlook doesn’t have to be bleak. As I mentioned, social distancing has supercharged digitalization and ecommerce. Cross-border ecommerce, in particular, has huge potential. It offers a new opportunity to reach billions of additional customers.
I believe that many companies overestimate the complexity of shipping their products abroad. Hurdles still exist, but taking a product to market on a global scale has, in fact, never been easier.
I am still surprised by the fact that of all the origin and destination country pairs there is still 25% with no recorded commerce at all. This makes it quite clear that many countries and firms still haven’t tapped into the benefits of increased connectedness, the potential gains from which can reach trillions of dollars. By connecting countries and corporations to new markets, ecommerce can be a powerful driver of additional growth and prosperity all over the world.
Reconnect for more resilience
As countries strive to recover from the impact of the virus, they will deal with economic hardship and political upheaval. Our industry has to take a stand. We need to articulate the value of trade and globalization and explain how they can bring prosperity to deprived communities, improving livelihoods and expectations around the world.
What is the World Economic Forum doing to manage emerging risks from COVID-19?
Technology enables us to mobilize the planet's resources and bring together human ingenuity to fight this and future crises. That’s why I believe the isolationist tendencies witnessed during this pandemic (whilst unavoidable some would say) will be transitory. The way globalization works is changing, but it is far from disappearing. This year’s DHL Global Connectedness Index validates all of this and more.
In fact, I still harbour a belief that 2020 will be remembered as the year the world grasped how much our well-being depends on global connection and collaboration. Let’s not see these changes as a lifeboat; let’s reimagine them as a growth rocket.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Stay up to date:
COVID-19
Forum Stories newsletter
Bringing you weekly curated insights and analysis on the global issues that matter.
More on Health and Healthcare SystemsSee all
Shyam Bishen
July 17, 2025