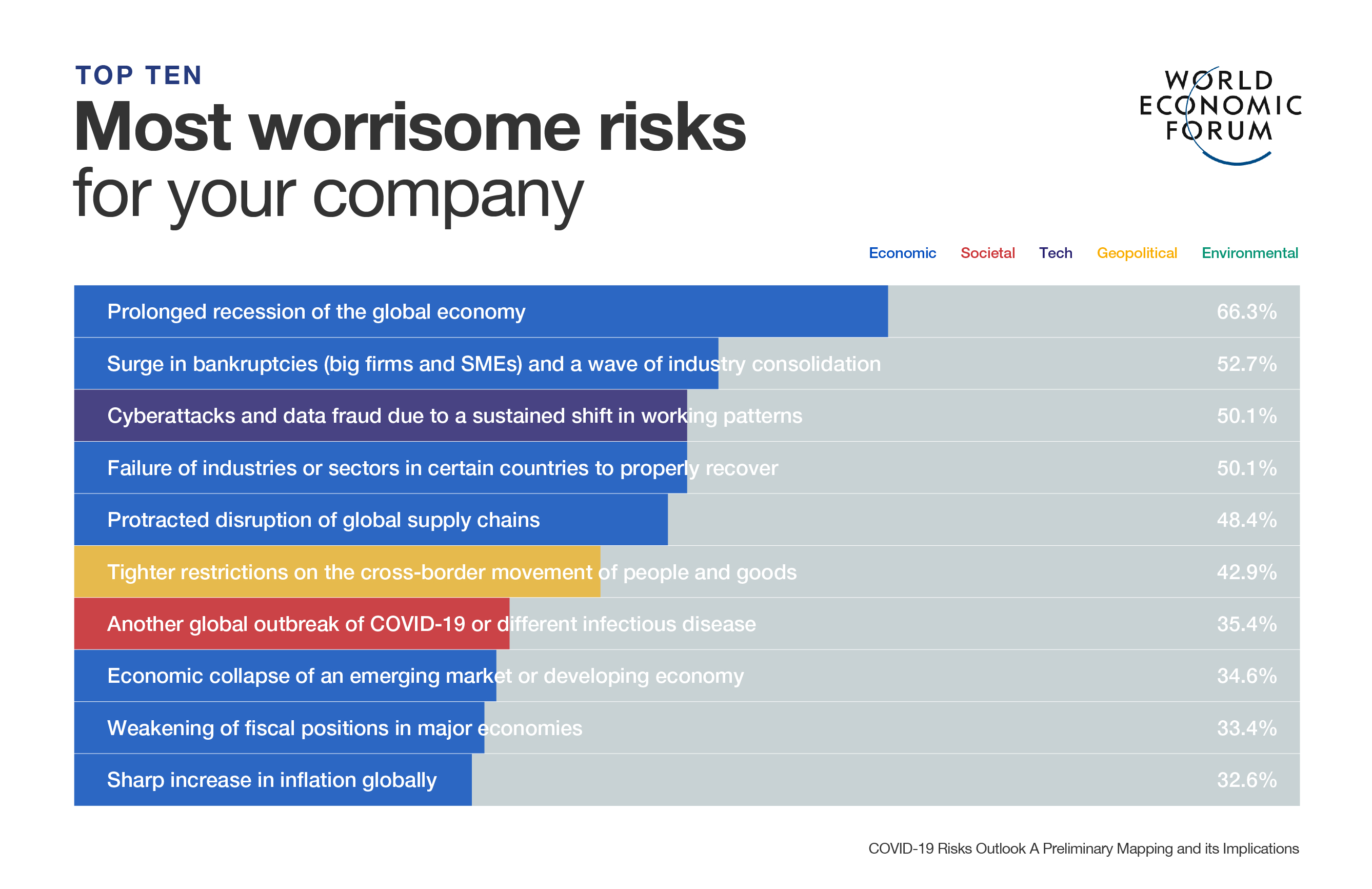
‘Untact’: South Korea’s plan for a contact-free society

Services in South Korea are being increasingly automated. Image: REUTERS/Kim Hong-Ji

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Republic of Korea
- South Korea’s government wants people to use contactless services in the fight to stop the spread of COVID-19 and to aid economic recovery.
- Contact-free customer experiences are becoming commonplace, and there’s even a word for it in South Korea: ‘untact’.
- ‘Untact’ services range from online shopping and ordering food remotely to telehealth.
In a cafe in Daejeon, South Korea, a robot barista serves drinks to reduce person-to-person contact between staff and customers.
It’s one example of an innovative solution to the difficulties of social distancing. But even before COVID-19, many kinds of contactless customer experience were becoming a feature of life in South Korea.
The march of ‘untact’ services
From online shopping and ordering food remotely to chatbots and appointments with virtual doctors, digital technologies have enabled the rise of services that minimize direct human interactions.
And in South Korea, there’s even a word for it: “untact”.
A term initially used by marketers, untact services are now being deployed in the fight to stop the spread of COVID-19 and to aid the country’s economic recovery.
What is the World Economic Forum doing to manage emerging risks from COVID-19?
The Digital New Deal – part of President Moon Jae-in’s $62 billion five-year Korean New Deal stimulus package – outlines plans to prepare for “surging demand for remote services”.
Projects to boost “untact industries” include building 18 smart hospitals for remote healthcare, providing digital care services for seniors and other vulnerable groups, helping small and medium-sized businesses set up virtual conferencing and online sales support for small companies.
There will also be investment in technologies that enable untact services, such as robotics, drones and high-speed internet.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Emerging TechnologiesSee all
James Fell
April 26, 2024
Alok Medikepura Anil and Uwaidh Al Harethi
April 26, 2024
Thomas Beckley and Ross Genovese
April 25, 2024
Robin Pomeroy
April 25, 2024
Beena Ammanath
April 25, 2024
Vincenzo Ventricelli
April 25, 2024