Retirement age trends around the globe

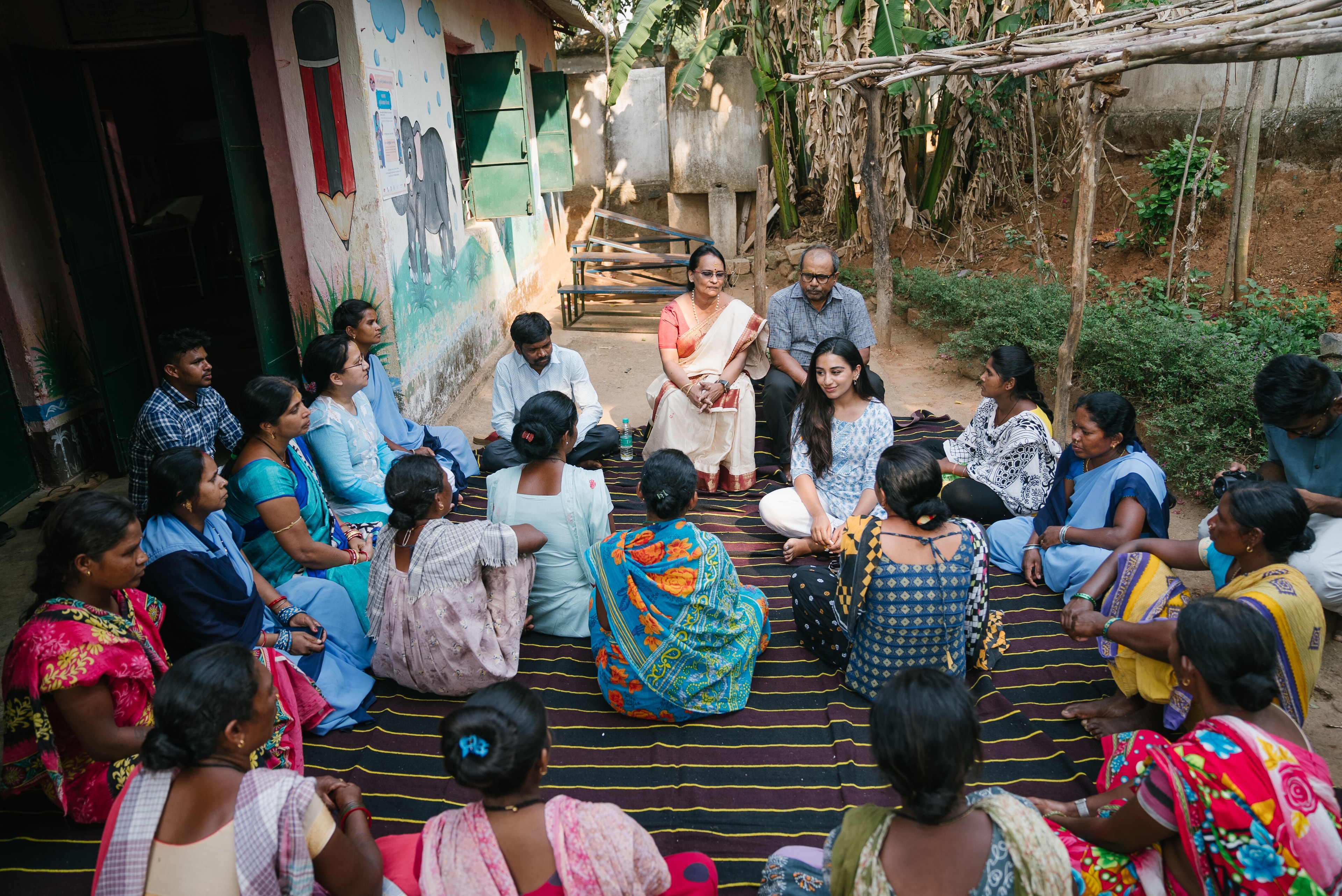
The OECD projects that the average effective retirement age will increase by two years by the mid-2060s. Image: Pexels/Centre for Ageing Better
Rida Khan
Financial Writer, Visual CapitalistOmri Wallach
Reporter, Visual CapitalistAlejandra Dander
Infographic Designer, Visual Capitalist
Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Health and Healthcare
- The retirement landscape varies greatly depending on the country.
- Many factors contribute to the variance between current and effective retirement ages.
- The OECD projects that the average effective retirement age will increase by two years by the mid-2060s.

Charted: Retirement age by country
The retirement landscape can look completely different depending on what country you’re in. And charting the retirement age by country reveals a lot of differences in the the makeup of a labor force, both for economic and cultural reasons.
This graphic delves into the current and effective retirement ages across 45 nations in 2020, based on comprehensive data from the OECD 2021 report.
Have you read?
Defining retirement ages
Before we dive into the numbers, let’s clarify the measurements used by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- The current retirement age is the age at which individuals can retire without penalty to pension after completing a full career starting from age 22.
- The effective retirement age refers to the average age of exit from the labor force for workers aged 40 years or more.
Many countries have seen workers effectively retire earlier or later than the current retirement age. This variance can arise due to a multitude in factors including differences in career start ages, some industries offering earlier retirements or benefits for later commitments, or countries facilitating different workforce exits due to market demands and policies.
Some people also choose to retire early due to personal reasons or a lack of available work, receiving a smaller pension or in some cases forgoing it entirely. Likewise, some people choose to stay employed if they are able to find work.
Retirement age by country in 2020
Here’s a snapshot of the current and effective retirement ages by country in 2020:





Three countries had the highest current retirement age at 67 years, Iceland, Israel, and Norway, but all had slightly lower effective retirement ages on average. On the flip side, Saudi Arabia had the lowest current retirement age at only 47 years with full pension benefits. Only Türkiye at 52 years was close, and notably both had much higher effective retirement ages on average.
Discrepancies between different regions are clear across the board. Many Asian countries including China, India, and South Korea have official minimum retirement ages in the early 60s and late 50s, but see workers stay in the workforce well into their late 60s. Meanwhile, most European countries as well as the U.S. and Canada have more workers retire earlier than minimum retirement ages on average.
Almost all of the countries with measured effective retirement ages for women also saw them exit the workforce earlier than men. This can be the result of cultural gender norms, labor force participation rates, and even the setup of pension systems in different countries.
The five exceptions in the dataset where women retired later than men? Argentina, Estonia, Finland, France, and Luxembourg.
Looking to the future
In 2023, France sparked controversy by raising its early retirement age by two years. This decision triggered widespread strikes and riots and ignited debates about the balance between economic sustainability and individual well-being.
Given aging demographics in many developed countries and a continued need for labor, this isn’t expected to be the only country to reassess retirement. The OECD projects a two-year increase in the average effective retirement age by the mid-2060s.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Health and Healthcare SystemsSee all
Kate Whiting
May 3, 2024
Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw
May 2, 2024
Johnny Wood
May 1, 2024
Prakash Tyagi
May 1, 2024
Katherine Klemperer and Anthony McDonnell
April 25, 2024