Our resources are running out. These charts show how urgently action is needed

“With decisive action by politicians and the private sector, a decent life for all is possible without costing the Earth," says the IRP’s Co-Chair, Janez Potočnik. Image: Unsplash/NASA

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Future of the Environment
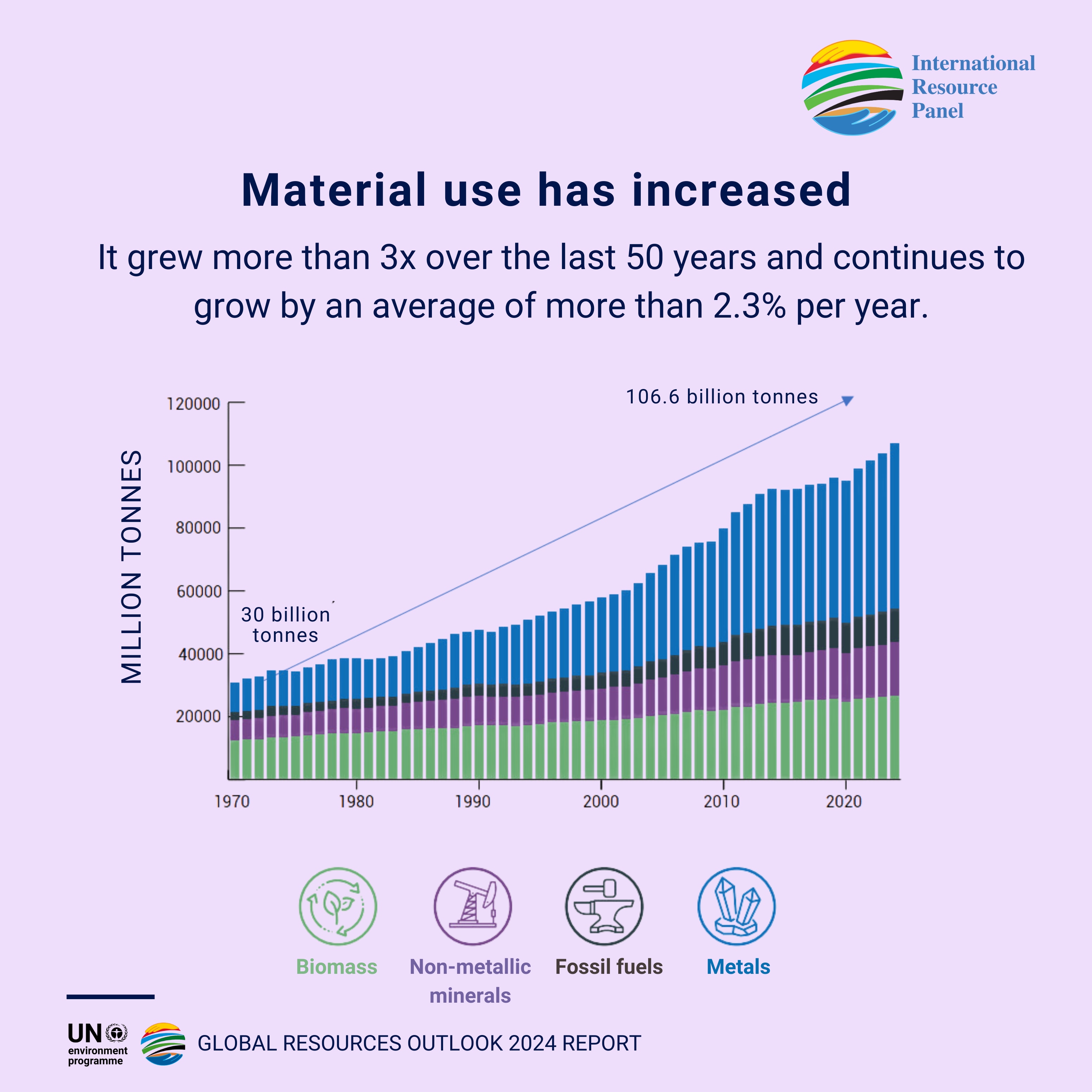
- Global natural resource consumption is forecast to rise 60% by 2060, compared with 2020 levels, according to the United Nations.
- Increasing demand for resources is due to urbanization, industrialization and a growing population, which is leading to severe consequences such as biodiversity loss, water stress, climate change and air pollution, it says.
- Disrupted supply chains for critical goods and resources were among the top risks identified in the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2024.
We’re racing into a resources crisis that’s set to intensify unless urgent action is taken.
Global natural resource consumption is predicted to increase by 60% by 2060, compared with 2020 levels, according to the United Nations Environment Programme's Global Resources Outlook, a report by the UN's International Resource Panel. That’s after material use grew more than three times over the past 50 years, it said.
Resources include crops for food, wood for energy, fossil fuels, metals like iron, aluminium and copper, non-metallic minerals, as well as land and water.
“It is no longer whether a transformation towards global sustainable resource consumption and production is necessary, but how to urgently make it happen,” said Janez Potocnik and Izabella Teixeirq, International Resource Panel (IRP) co-chairs.

The pace at which we’re using our planet’s resources has a connection to almost every aspect of our lives. This exploitation is the main driver for the triple planetary crises, which are defined by the United Nations as the climate crisis, biodiversity loss and the pollution crisis, according to the IRP.
How is the World Economic Forum contributing to build resilient supply chains?
Disrupted supply chains for critical goods and resources were among the top risks identified in the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2024 for the current risk landscape. Environmental risks were another significant concern identified in that report, with extreme weather ranked as the top risk likely to cause a global crisis in 2024.
Even so, the writers of the report still see scope to reduce resource use while growing the economy and achieving the other UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This will require a “decoupling” so that the environmental impacts of resource use fall, while the well-being contributions increase, they say.
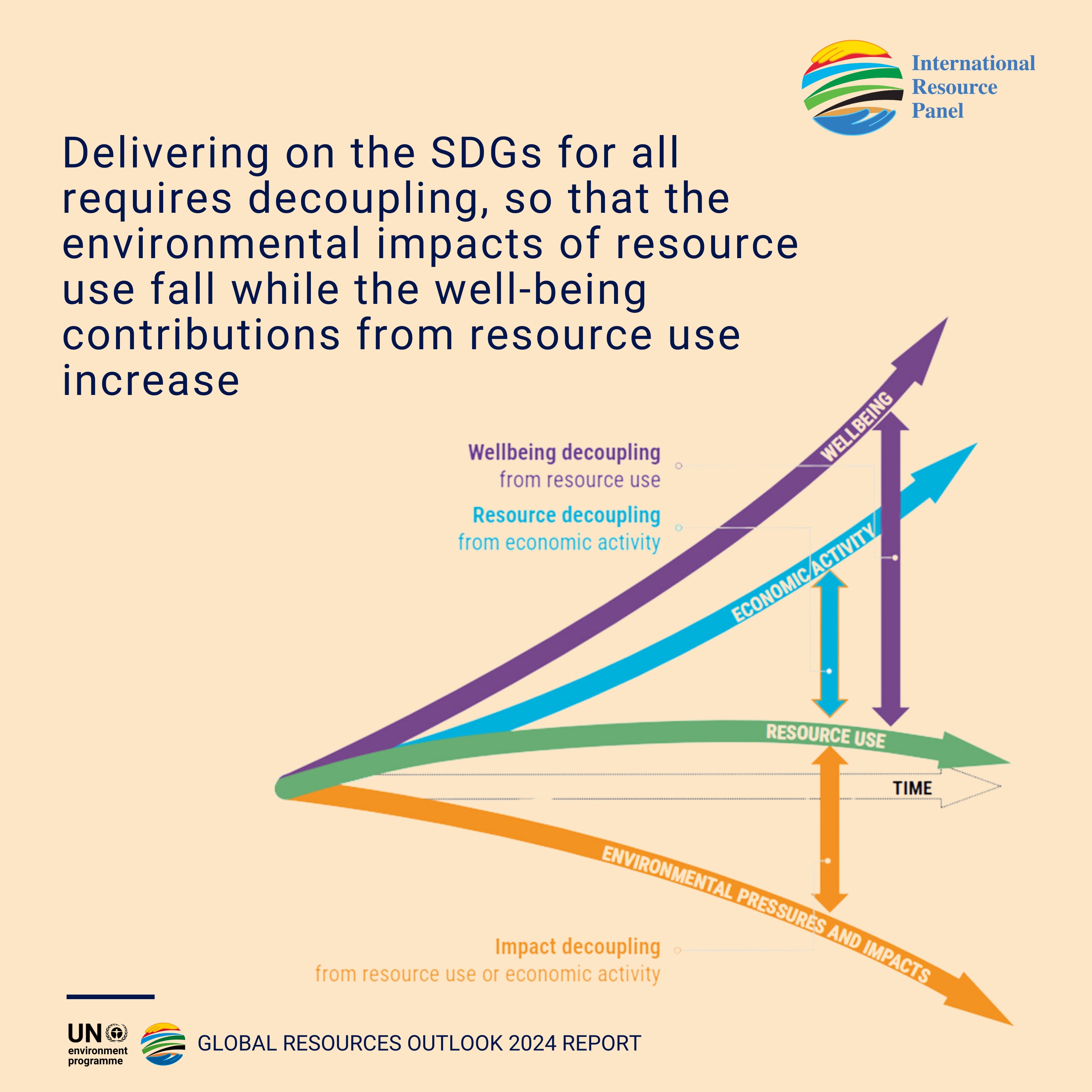
“Reorienting demand and allowing resource use to grow where it is most needed will open pathways to achieving the SDGs and a shared and equitable prosperity for all,” the report says. Bold policy action will be required and there must be a “much stronger focus on demand-side – consumption – measures”.
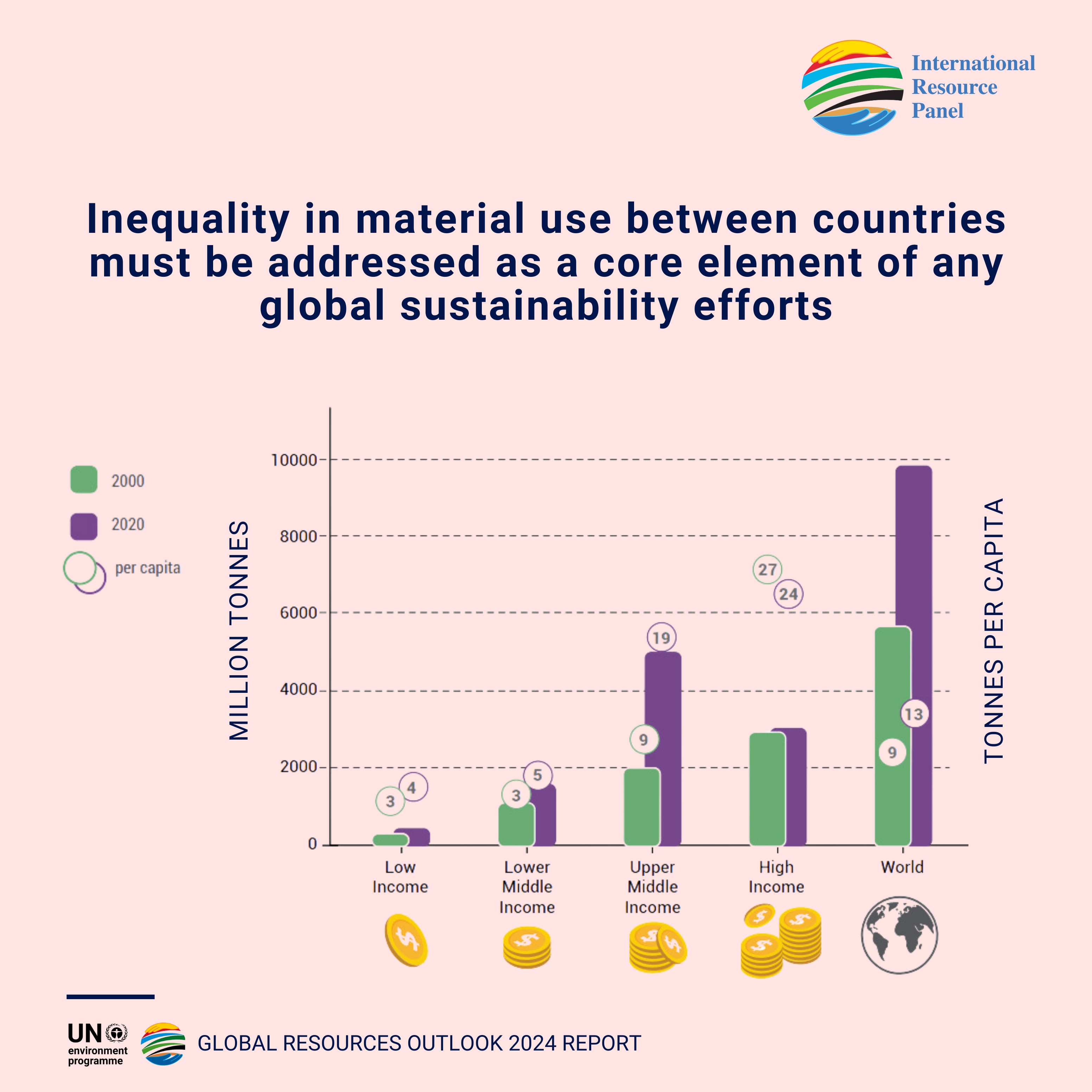
High-income countries use six times more materials per capita and are responsible for 10 times more climate impacts per capita than low-income countries. Material inequalities must be addressed as a core element of any approach, the report warns.
In areas where consumption levels are high, there needs to be a focus on lowering resource and material consumption levels and on efficiency. This could help reduce around 30% of resource use around the world compared with historical trends, it says. In countries where resource use needs to grow, it is possible to use strategies that maximize the value we get from resources.
Directing finance towards sustainable resource use is one potential solution, the report suggests, by making sure the true costs of resources are reflected in the structure of the economy. Providing consumers with information and access to sustainable goods and services is also crucial.
Regulation has an important role to play in disincentivizing or banning resource-intensive options – for example non-essential single-use plastic products, the report points out. Business models that build in refuse, reduce, eco-design, reuse, repair, and recycling initiatives are also necessary.
Much needs to be done to transform our built environments, and the ways we move around, and consume food and energy. High- and upper-middle-income countries could also shift away from animal protein.
“We should not accept that meeting human needs must be resource intensive, and we must stop stimulating extraction-based economic success,” said the IRP’s Co-Chair, Janez Potočnik. “With decisive action by politicians and the private sector, a decent life for all is possible without costing the Earth.”
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Sustainable DevelopmentSee all
Johnny Wood
April 15, 2024
Robin Pomeroy and Sophia Akram
April 10, 2024
Eliane Trindade
April 4, 2024
Chirag Chopra and Piyush Gupta
April 2, 2024
Lisa Satolli
April 2, 2024