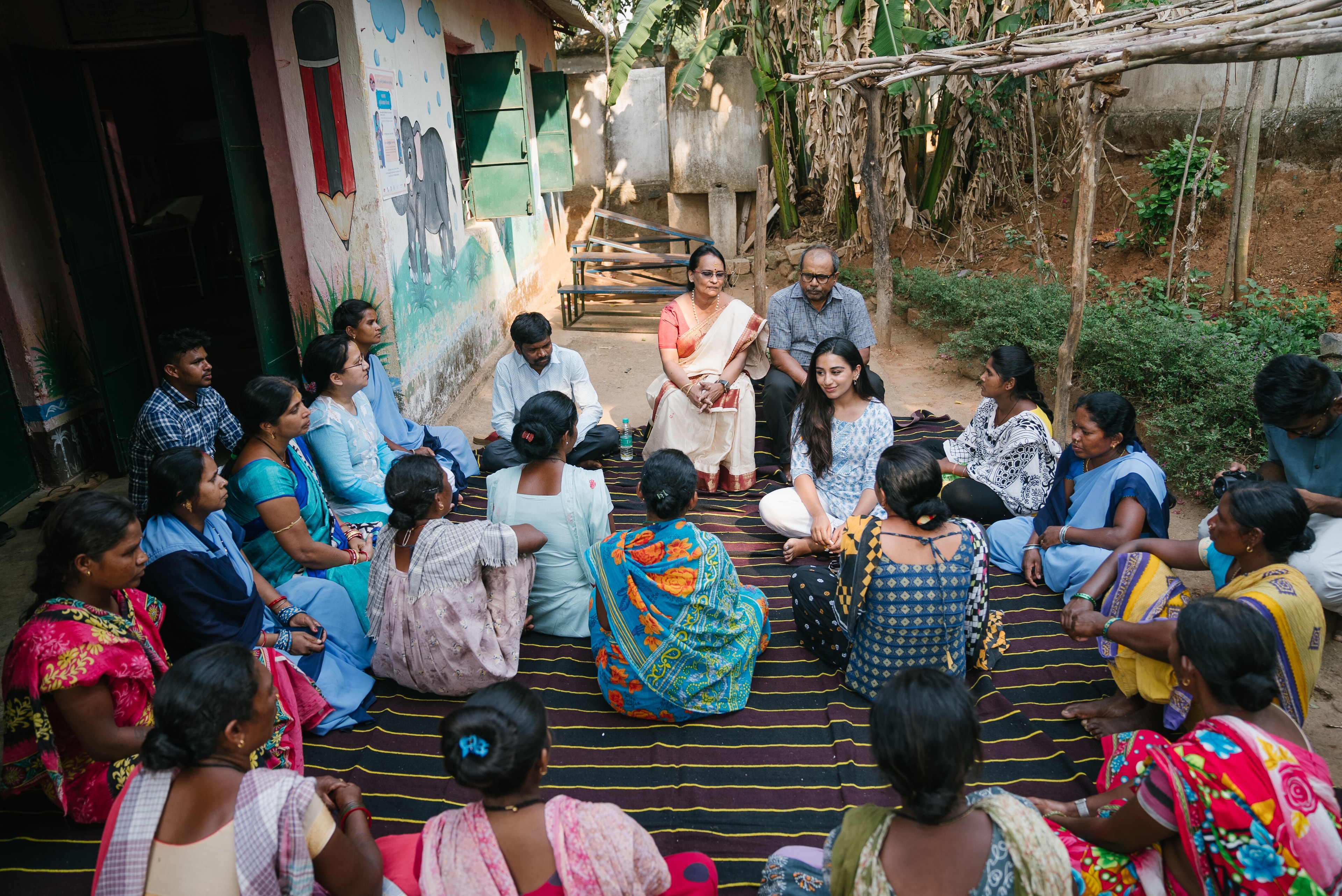
How our level of personal resilience changes over time

New research suggests that resilience fluctuates over time. Image: Unsplash/Ameer Basheer

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Education, Gender and Work
- Researchers at North Carolina State University suggest that resilience is more of a process than a characteristic.
- They also report that resilience fluctuates, encompassing the way that an individual responds to a variety of circumstances over time.
- The work also shows that resilience can wear down over time, even if people are only exposed to mild stressors.
Resilience is a dynamic process, rather than a fixed trait, a new study finds.
“Our work here does a couple things,” says Patrick Flynn, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of human resources management at North Carolina State University’s Poole College of Management.
“First it finds that resilience is more of a process than a characteristic. Second, it identifies some of the characteristics that can contribute to that process in a meaningful way. Taken together, we think the findings can inform recruitment, hiring, operations, and training practices.”
At the heart of the study is the idea that resilience fluctuates, because it encompasses the way that an individual responds to a variety of circumstances over time.
“It’s impossible to assess dynamic resilience at any given moment,” Flynn says. “Dynamic resilience is demonstrated across time. How does people’s behavior change over time? What influences that? Those are the sorts of questions we wanted to answer with this study.”
To that end, researchers worked with 314 members of a university marching band. Study participants were surveyed weekly for 12 weeks. The surveys were designed to collect data on individual participants and their emotional and personal characteristics. To assess how resilience is functioning in individuals over time, the researchers also asked study participants about their commitment to the marching band as an organization, as well as their feelings of “burnout”—specifically, emotional exhaustion related to their work in the organization.
“Tracking the trajectories of commitment and burnout helped us see how resilience played out in real world terms,” Flynn says.
“Organizations are interested in cultivating a resilient workforce, because they want people who are able to remain committed to an organization and its goals over time.”
The researchers found that, on average, emotional exhaustion increased over time and commitment decreased over time. However, there were factors that influenced those effects.
For example, experience within the organization exacerbated the effects of emotional exhaustion and decreased commitment. In other words, newcomers appeared to be more resilient over the study period.
The researchers also found that people who scored higher on assessments of emotional stability were better able to maintain higher levels of commitment.
Lastly, the researchers also looked at the trajectory of each individual’s commitment to the organization to see if it predicted “retention.” They found that positive commitment trajectories were associated with a greater likelihood of both planning to return to the organization for another year and then subsequently doing so.
“One takeaway here is that annual employee surveys may not be the best way to assess employee resilience and commitment to an organization,” Flynn says.
That’s because annual surveys provide snapshots, while resilience is a dynamic process that fluctuates.
“Since resilience affects things like employee retention, which are important to a company’s bottom line, we really need to be touching base with employees more often,” Flynn says.
The work also shows that resilience can wear down over time, even if people are only exposed to mild stressors.
“Chronic stress can wear down resilience, with ramifications for employee retention and, in all likelihood, job performance,” Flynn says.
“However, we also feel that thinking about resilience as a dynamic process creates opportunities to foster resilience in employees not only through recruitment, but through training, and even job design. In short, it’s not as simple as hiring the right person and assuming things will work out. Fostering resilience is going to be an ongoing task for management and human resources professionals.”
The paper appears in the journal Group & Organization Management. Coauthors are from the University of South Carolina. The work took place with support from the Riegel and Emory HR Center at USC’s Darla Moore School of Business.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Wellbeing and Mental HealthSee all
Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw
May 2, 2024
Kate Whiting
April 17, 2024
Adrian Gore
April 15, 2024
Fatemeh Aminpour, Ilan Katz and Jennifer Skattebol
April 15, 2024
Andrew Moose and Ruma Bhargava
April 5, 2024