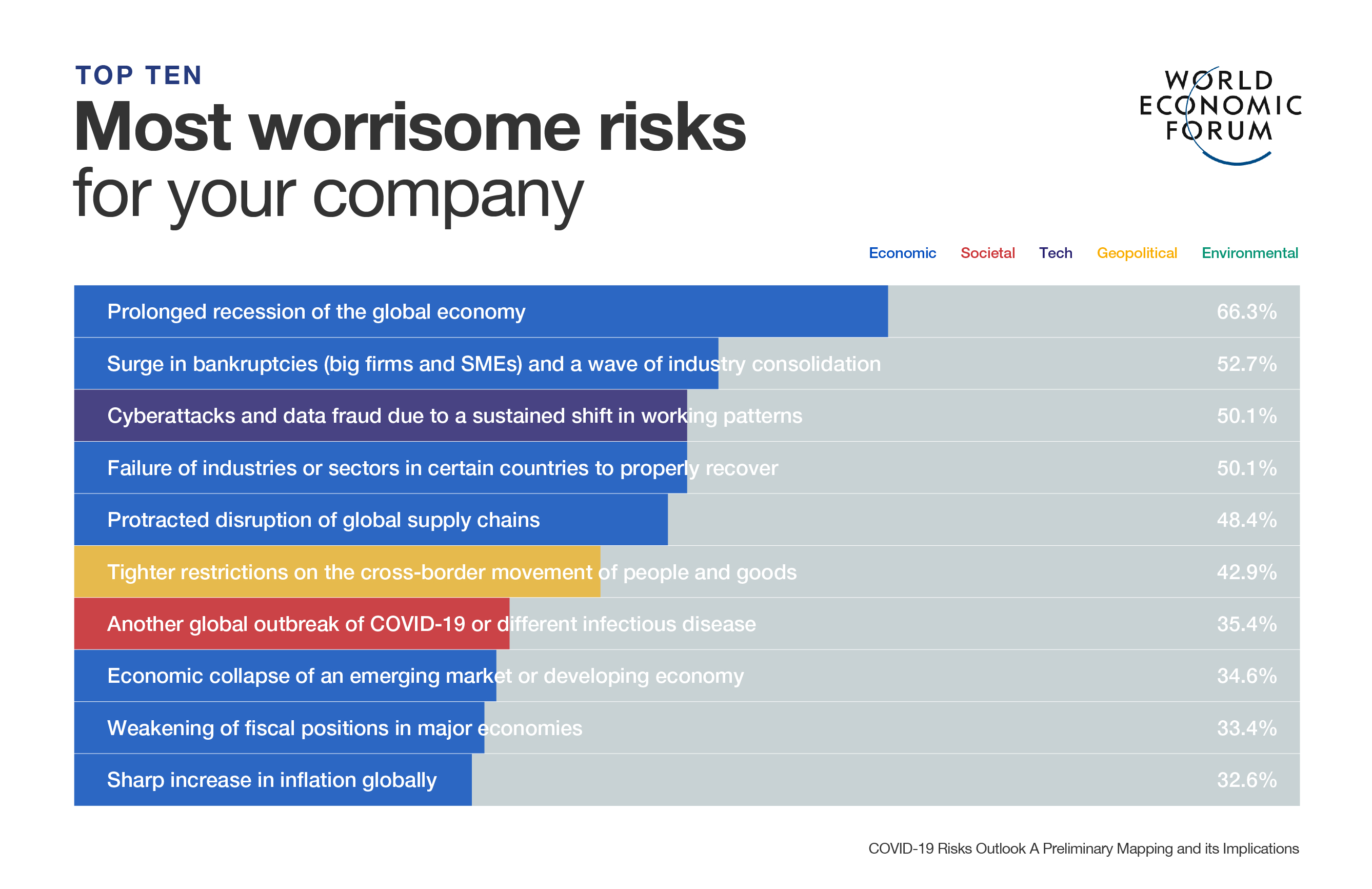
5 charts that show the worst may be over for coronavirus and global trade

The WTO's April forecast predicted trade could fall by 32%. Image: REUTERS
- World trade fell steeply in the first half of 2020 as the COVID-19 pandemic hit.
- Government and central bank intervention helped stem the losses.
- World Trade Organization economists now say we have avoided the worst-case scenario.
- Risks to the outlook include a second wave of COVID‑19 or trade restrictions.
The worst-case scenario for global trade in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic has been avoided, according to economists from the World Trade Organization (WTO).
After the volume of merchandise trade shrank by 3% year-on-year in the first quarter, estimates for the second quarter - when lockdown measures affected the largest share of the global population - show a drop of 18.5%.
“These declines are historically large, but could have been much worse,” the WTO says on its website. The organization’s April forecast predicted trade could fall by 32% in a worst-case scenario.
Even so, there are risks to the outlook, including a second wave of COVID‑19, weaker economic growth, and governments imposing trade restrictions.
What is the World Economic Forum doing to manage emerging risks from COVID-19?
“There is an important silver lining here: it could have been much worse,” said WTO Director-General Roberto Azevêdo.
“For output and trade to rebound strongly in 2021, fiscal, monetary, and trade policies will all need to keep pulling in the same direction.”
This echoes the sentiment of the World Economic Forum initiative The Great Reset, which identifies a “unique window of opportunity to shape the recovery” and stresses the need for national leaders and businesses to define common objectives.
Here are 5 charts that illustrate the WTO’s view of how global trade has been affected.
1. Trade may have bottomed out in the second quarter of 2020
The WTO's April forecast showed two pathways: an optimistic scenario where world trade fell 13% in 2020, and a pessimistic one where trade fell 32%. The latter has been avoided, it says, and trade only needs to grow by 2.5% per quarter for the rest of this year to meet the optimistic projection.
2. Global commercial flights carrying air cargo have started to rise again
The number of flights fell 74% between 5 January and 18 April, but have since risen. While these increases are from historic lows, container-port throughput also looks like it is recovering, the WTO says, and other indicators of exports show some improvement.
3. More containers are on the move
While container-port throughput showed a partial recovery, that followed near-historic declines, and the WTO says it’s too early to draw any definitive conclusions.
4. Indices of new export orders started to recover in May
After record drops, purchasing managers' indices showed export orders started to recover in May.
5. Signs of better auto sales
Automobile sales also show signs of recovery from lows. Sales of cars in China fell almost 80% in February compared with a year earlier, but rose 5% year-on-year in May. Declines in car sales in Western Europe and the US slowed in May.
The WTO says these tentative signs of recovery will be monitored closely as lockdowns are lifted around the world, and economies start to open up.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Stay up to date:
Economic Growth
Forum Stories newsletter
Bringing you weekly curated insights and analysis on the global issues that matter.
More on Economic GrowthSee all
Rishika Daryanani, Daniel Waring and Tarini Fernando
November 14, 2025