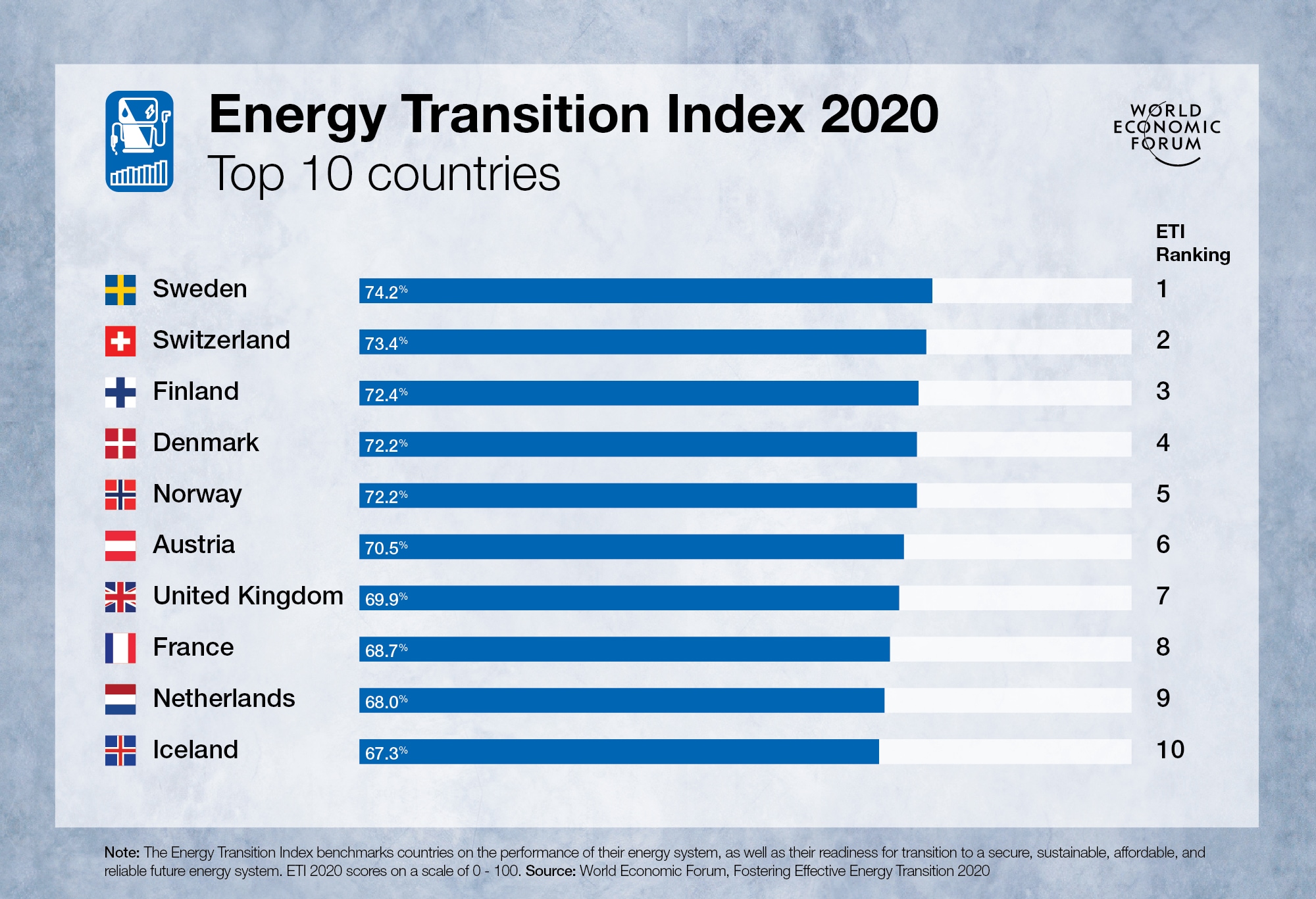
Here's how the food and energy crises are connected

The link between climate, food and energy can no longer be ignored. Image: World Economic Forum

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Sustainable Development
Listen to the article
- President Biden has announced $2.9 billion in additional US funding to combat global food insecurity.
- The food and energy crises are interlinked: fertilizer production has been halted because of the soaring cost of natural gas, which the industry needs to create ammonia.
- The World Economic Forum's Sustainable Development Impact Meetings are addressing the energy and food crises: panellists say the link between climate, food and energy can no longer be ignored at the Food and Energy: Tackling a Global Resource Crisis session.
Global food prices hit a record high in March, and the number of people facing acute food insecurity has more than doubled since 2019, according to the World Food Programme, as COVID-19, conflict and the climate crisis combined to impact our food systems.
The Global Hunger Index demonstrates how the knock-on effect of the war in Ukraine on supplies and prices of food, fertilizer, and fuel is exacerbating the food crisis, worsening hunger in 2023 and beyond. Many nations rely on Russia and Ukraine for the bulk of their wheat imports.
As part of the World Economic Forum's Sustainable Development Impact Meetings, experts came together to discuss the fragility of our interconnected global resource system in a session called Food and Energy: Tackling a Global Resource Crisis.

The session took place as the United Nations General Assembly in New York hosted an address from President Biden, who announced $2.9 billion in additional US funding to combat global food insecurity, building on $6.9 billion in US food security funding already committed this year.
The panellists were: Máximo Torero, Chief Economist of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); Jason Bordoff, Co-Dean of Columbia Climate School and Founding Director of the Center on Global Energy Policy, Columbia University; Geraldine Matchett, Co-Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of Royal DSM; and Sam Kass, Partner at Acre Venture Partners.
These were some of the key quotes from the session:
Food needs to be included in climate discussions
"This last year has shown us a window into the future: the future is here and now," said Sam Kass.
"These massive disruptions that are having ripple effects around the world are the norm, and it's just a taste of what we're going to have to manage going forward in more intense ways. I hope it's a wake-up call to policy-makers around just what's at stake when it comes to food security and the impact and intersection between food and climate.
"Food's been left out of the dialogue almost entirely: it's the number two driver of emissions globally, it's also the system most directly affected by climate itself. What's emerging in our food system is an opportunity to help solve the climate crisis, unlike any other sector ... there are very few sectors that can have a net-positive result on sequestering carbon."
Conflict, COVID-19 and the related economic downturn, and climate change are the main drivers of food insecurity, and they interact, said Máximo Torero. Climate change has two dimensions: extremes such as flooding, which are currently affecting Pakistan, and variability, which makes it very difficult for farmers to make decisions. This is where technology could help.
How the food and energy crises are connected
Torero said there is a serious problem of food access this year, with 1.72 billion people at risk.
But we have also "forgotten" the link between energy and food, he said. "We talk about the changing energy mix for climate issues, but that will increase the price of energy, of natural gas, and that will increase the price of fertilizer. That is what really is putting at risk the next supply and could create a problem of food availability as well as access."
Jason Bordoff said rising energy costs are driving up cooking fuel costs, but also the costs of making fertilizer, which is affecting food production.
It's the first "global energy crisis" – what's happening in Europe is having ripple effects, pushing up prices in the developing world and emerging markets.
"Natural gas is used for cooking, heating and fertilizer, that's how we grow food. Around 70% of fertilizer production in Europe is shut down, because there's not enough energy because it's too expensive ...
"When you're facing scarce energy sources, the first thing politicians do is let people keep heating their homes ... and shut down industry. Fertilizer is a big part of industry and that's going to have a big impact in poorer parts of the world in terms of food production."
What's the World Economic Forum doing about the transition to clean energy?
Geraldine Matchett added that producing food without fertilizer reduces yields by 50%, and that the current fertilizer situation is not just an access problem but an availability problem.
Ten fertilizer plants in Europe have closed, said Torero, meaning Europe will go from an exporter of nitrogen to a net importer, which will affect the poorest.
Matchett said what gives her hope is that people are now "leaning in" on regenerative agriculture – and cooperating.
"Having COP27 and COP28 coming up is really helpful. There’s a full awareness that climate, food and energy all hang together. I'm really hopeful that now we're going to have the right conversations. It’s been very much a siloed energy discussion, as if energy is a standalone thing.
"We have seen when food fails, everything fails ... Food is a daily requirement ... If there's one thing that unites populations around the world, it's not only the need for food, it's the passion for food. It's at the core. If we bring to COP27 and COP28 the passion ... hopefully we can break through some of these geopolitical barriers."
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Sustainable DevelopmentSee all
Robin Pomeroy and Sophia Akram
April 10, 2024
Eliane Trindade
April 4, 2024
Chirag Chopra and Piyush Gupta
April 2, 2024
Lisa Satolli
April 2, 2024
Pooja Chhabria
March 28, 2024
Andrea Willige
March 27, 2024