The Future of Jobs Report 2023

1. Introduction: the global labour market landscape in 2023
The past three years have been shaped by a challenging combination of health, economic and geopolitical volatility combined with growing social and environmental pressures. These accelerating transformations have and continue to reconfigure the world’s labour markets and shape the demand for jobs and skills of tomorrow, driving divergent economic trajectories within and across countries, in developing and developed economies alike. The Fourth Industrial Revolution, changing worker and consumer expectations, and the urgent need for a green and energy transition are also reconfiguring the sectoral composition of the workforce and stimulating demand for new occupations and skills. Global supply chains must also quickly adapt to the challenges of increasing geopolitical volatility, economic uncertainty, rising inflation and increasing commodity prices.
Like previous editions, The Future of Jobs Report 2023 offers insights into these transformations and unpacks how businesses are expecting to navigate these labour-market changes from 2023 to 2027, leveraging a unique cross-sectoral and global survey of Chief Human Resources, Chief Learning Officers and Chief Executive Officers of leading global employers and their peers.
This report is structured as follows: Chapter 1 reviews the global labour-market landscape at the beginning of 2023. Chapter 2 explores how key macrotrends are expected to transform this landscape over the 2023–2027 period. Chapters 3 and 4 then discuss the resulting global outlooks for jobs and skills over the 2023–2027 period. Chapter 5 reviews emerging workforce and talent strategies in response to these trends. The report’s appendices provide an overview of the report’s survey methodology and detailed sectoral breakdowns of the five-year outlook for macrotrends, technology adoption and skills.
In addition, The Future of Jobs Report 2023 features a comprehensive set of Economy, Industry, and – for the first time – Skill Profiles. User Guides are provided for each of these profiles, to support their use as practical, standalone tools.
As a foundation for analysing respondents’ expectations of the future of jobs and skills in the next five years, this chapter now assesses the current state of the global labour-market at the beginning of 2023.
Diverging labour-market outcomes between low-, middle- and high-income countries
The intertwined economic and geopolitical crises of the past three years created an uncertain and divergent outlook for labour markets, widening disparities between developed and emerging economies and among workers. Even as a growing number of economies have begun to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic and its associated lockdowns, low- and lower-middle-income countries continue to face elevated unemployment, while high-income countries are generally experiencing tight labour markets.
At the time of publication, the latest unemployment rates stand below pre-pandemic rates in three quarters of OECD countries,1 and across a majority of G20 economies (Figure 1.1). At 4.9%, the 2022 unemployment rate across the OECD area is at its lowest level since 2001.2
By contrast, many developing economies have experienced a comparatively slow labour-market recovery from the disruptions induced by the COVID-19 pandemic. In South Africa, for example, the formal unemployment rate has climbed to 30%, five percentage points higher than it was pre-pandemic (Figure 1.1). Developing economies, especially those reliant on the sectors hardest hit by recurring lockdowns, such as hospitality and tourism, still exhibit slow labour-market recoveries.
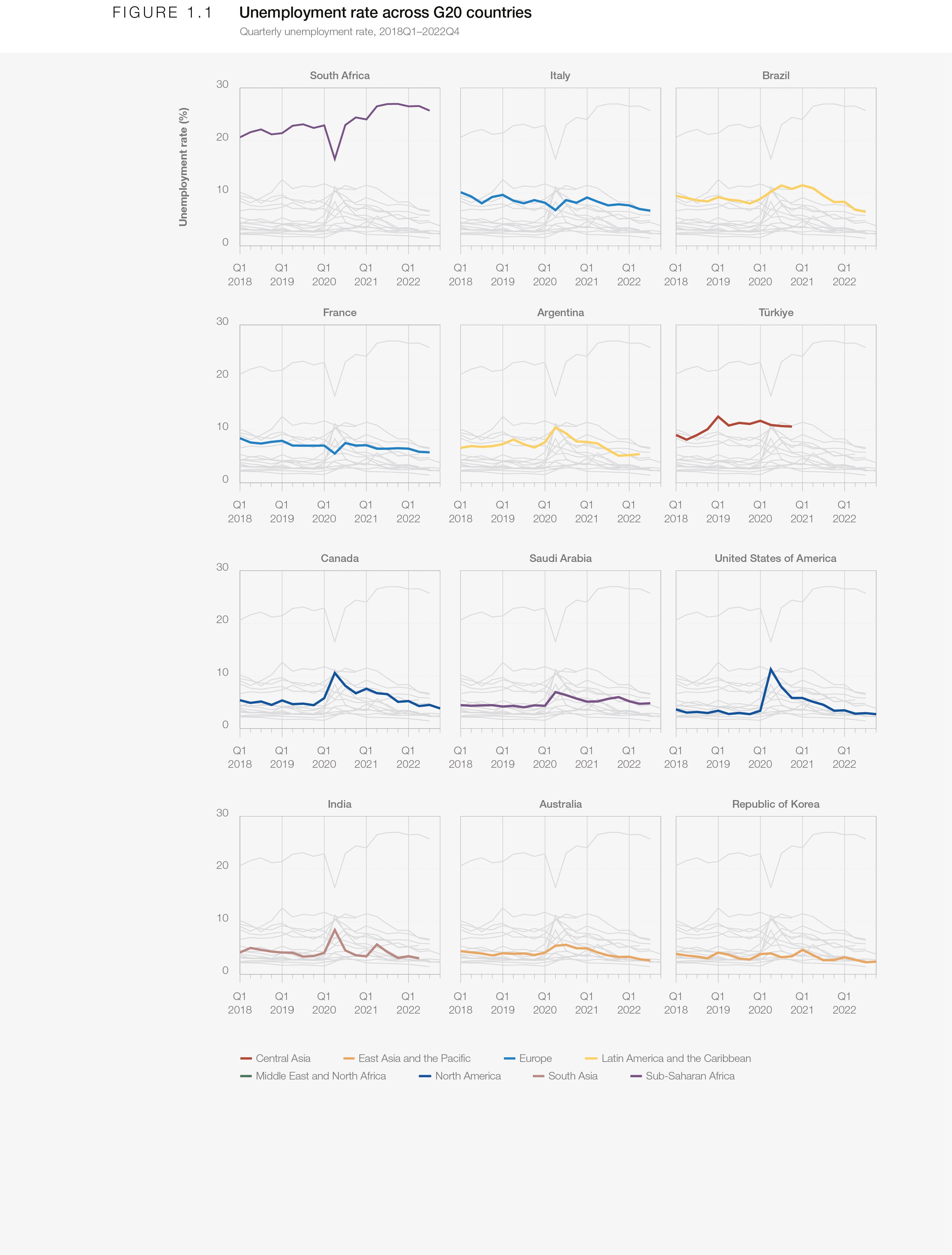

The asymmetry of the recovery is exacerbated by countries’ varying capacities to maintain policy measures to protect the most vulnerable and maintain employment levels. While advanced economies were able to adopt far-reaching measures, emerging economies have provided less support to the most vulnerable firms and workers due to their limited fiscal space.3,4
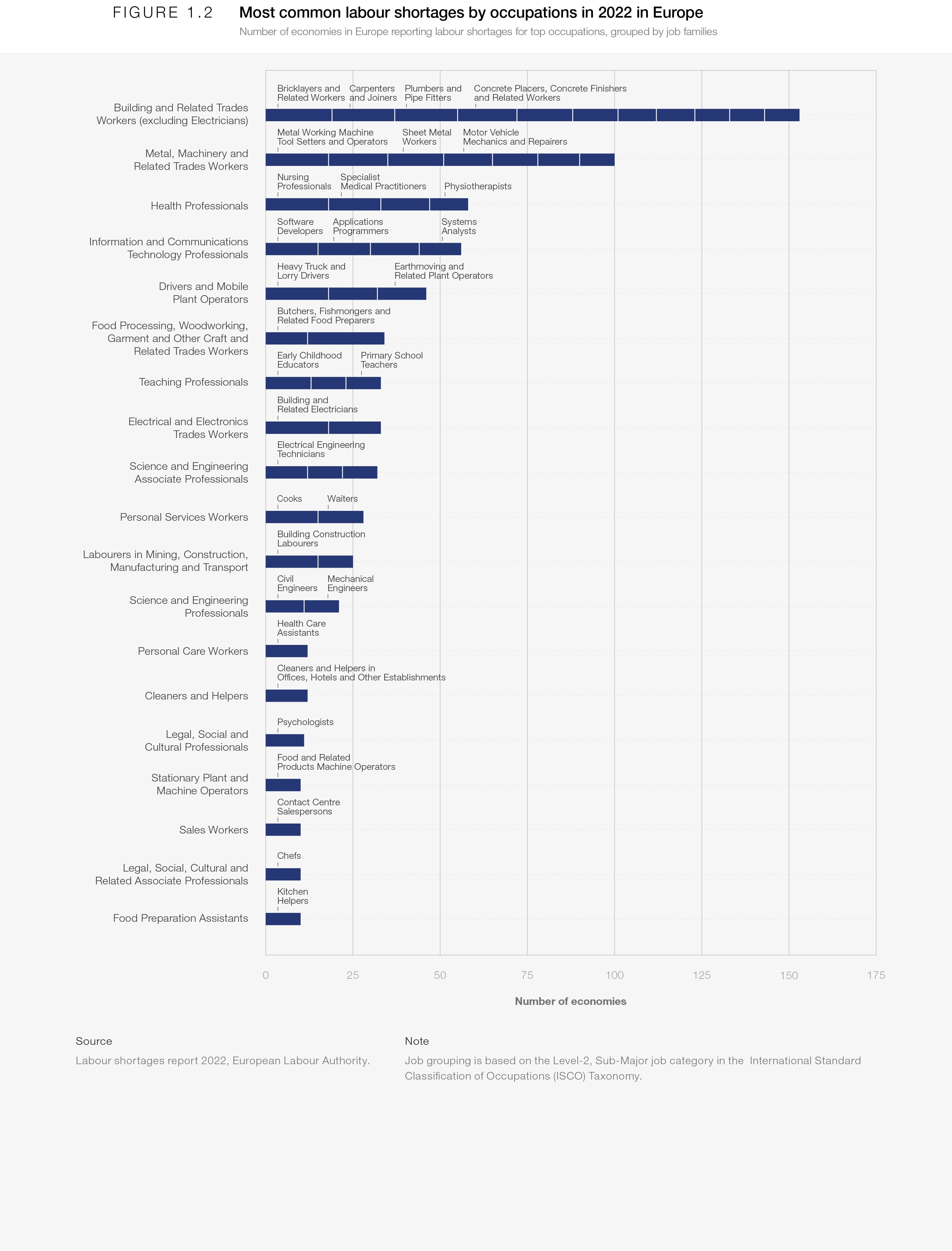
In 2022, various employment indicators pointed towards a strong labour-market recovery for high-income countries, with many sectors experiencing labour shortages. In Europe, for example, almost three in 10 manufacturing and service firms reported production constraints in the second quarter of 2022 due to a lack of workers.5 Nursing professionals, plumbers and pipefitters, software developers, systems analysts, welders and flame cutters, bricklayers and related workers, and heavy truck and lorry drivers were among the most needed professions (Figure 1.2).
In the United States, businesses in Retail and Wholesale of Consumer Goods reported close to 70% of job openings remaining unfilled, with close to 55% of roles unfilled in manufacturing and 45% in leisure and hospitality.6 Businesses also reported difficulties in retaining workers. According to a global survey conducted in late 2022 across 44 countries, one in five employees reported they intend to switch employers in the coming year.7
Diverging employment levels by gender, age and education level
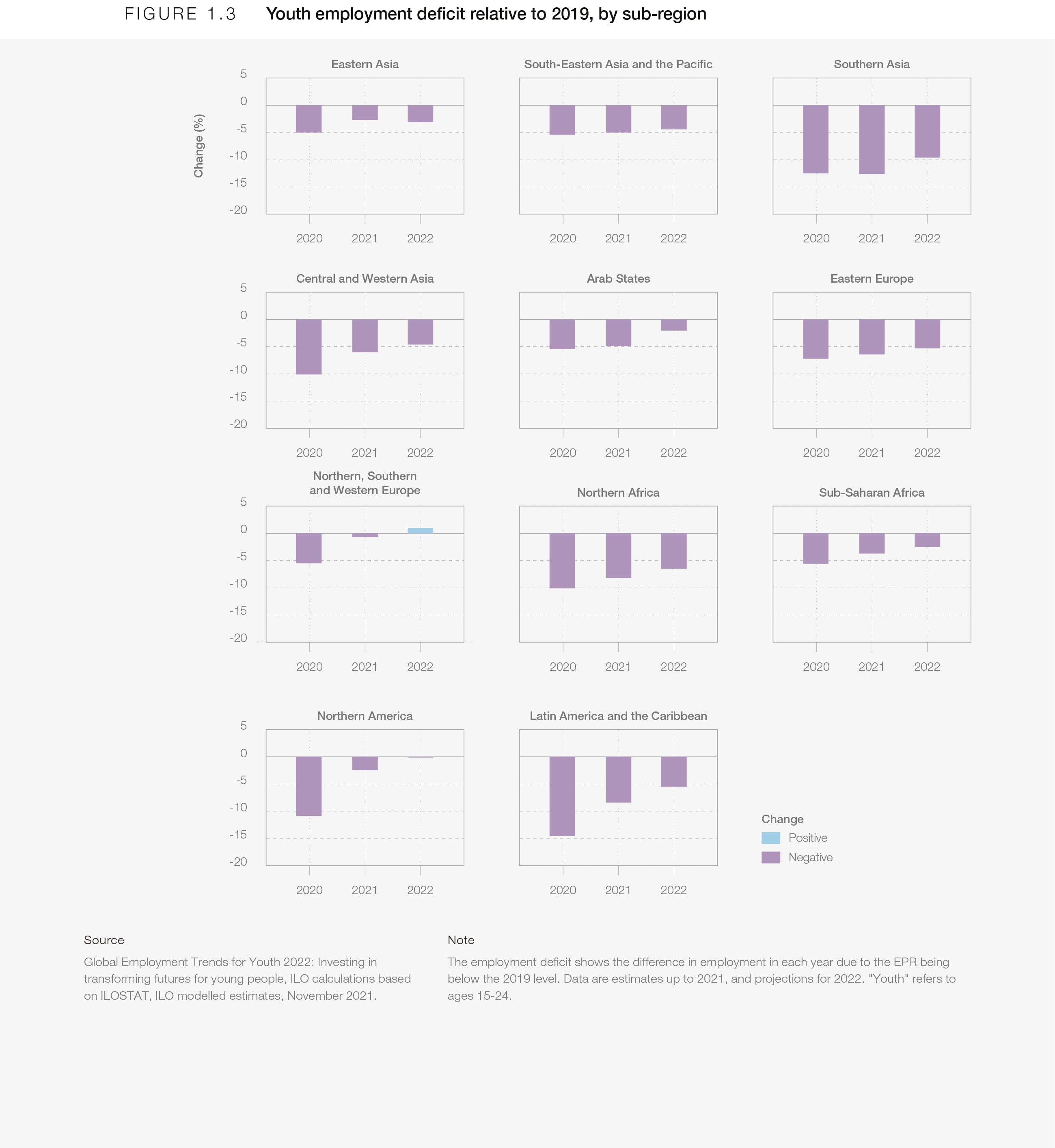
Women experienced greater employment loss than men during the pandemic8, and according to the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 20229, gender parity in the labour force stands at 62.9% – the lowest level registered since the index was first compiled. The global pandemic also disproportionately impacted young workers, with less than half of the global youth employment deficit projected to have recovered by the end of 2022.10 As highlighted in Figure 1.3, the youth employment deficit relative to 2019 is largest in Southern Asia, Latin America, Northern Africa and Eastern Europe, with only Europe and North America likely to have fully recovered at the time of publication.
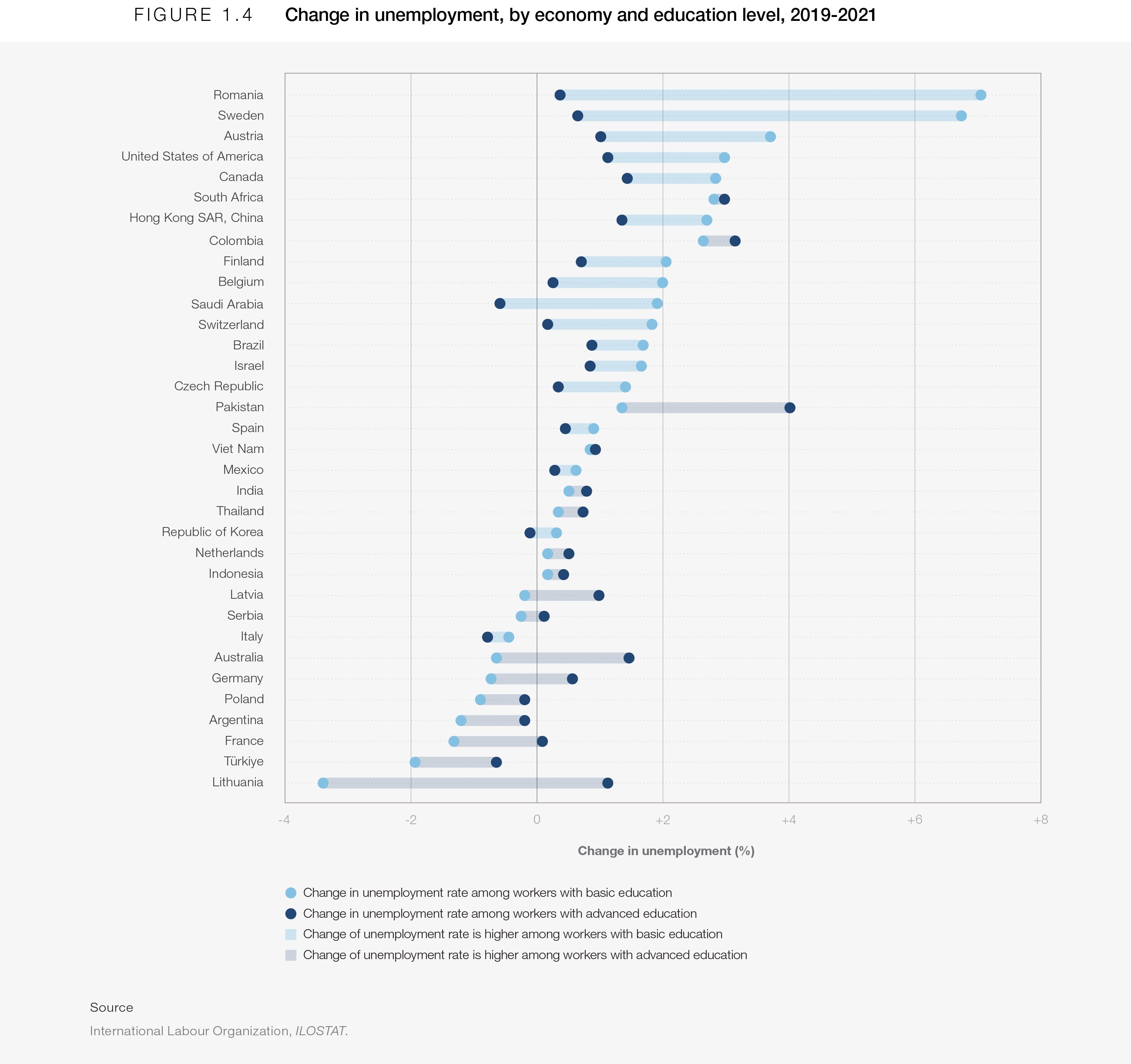
Workers with a basic education were also hardest hit in 2020, and slower to recover their prior participation in the labour market. In many countries the increase in unemployment from 2019 to 2021 of workers with a basic education level was more than twice as large as the impact on workers with advanced education (Figure 1.4).
Access to social protection
From January 2020 to January 2022, almost 3,900 social-protection measures were implemented across 223 economies to support the labour force impacted by COVID-19.11 These measures are estimated to have reached close to 1.2 billion people globally. Wage subsidies, cash transfers, training measures and extending unemployment-benefit coverage have all been crucial tools to protect the most vulnerable during the pandemic. Most such short-term support measures are now being phased out,12 and targeted medium to long-term investments will be needed to alleviate the long-term effects of recurring economic shocks on firms and workers.
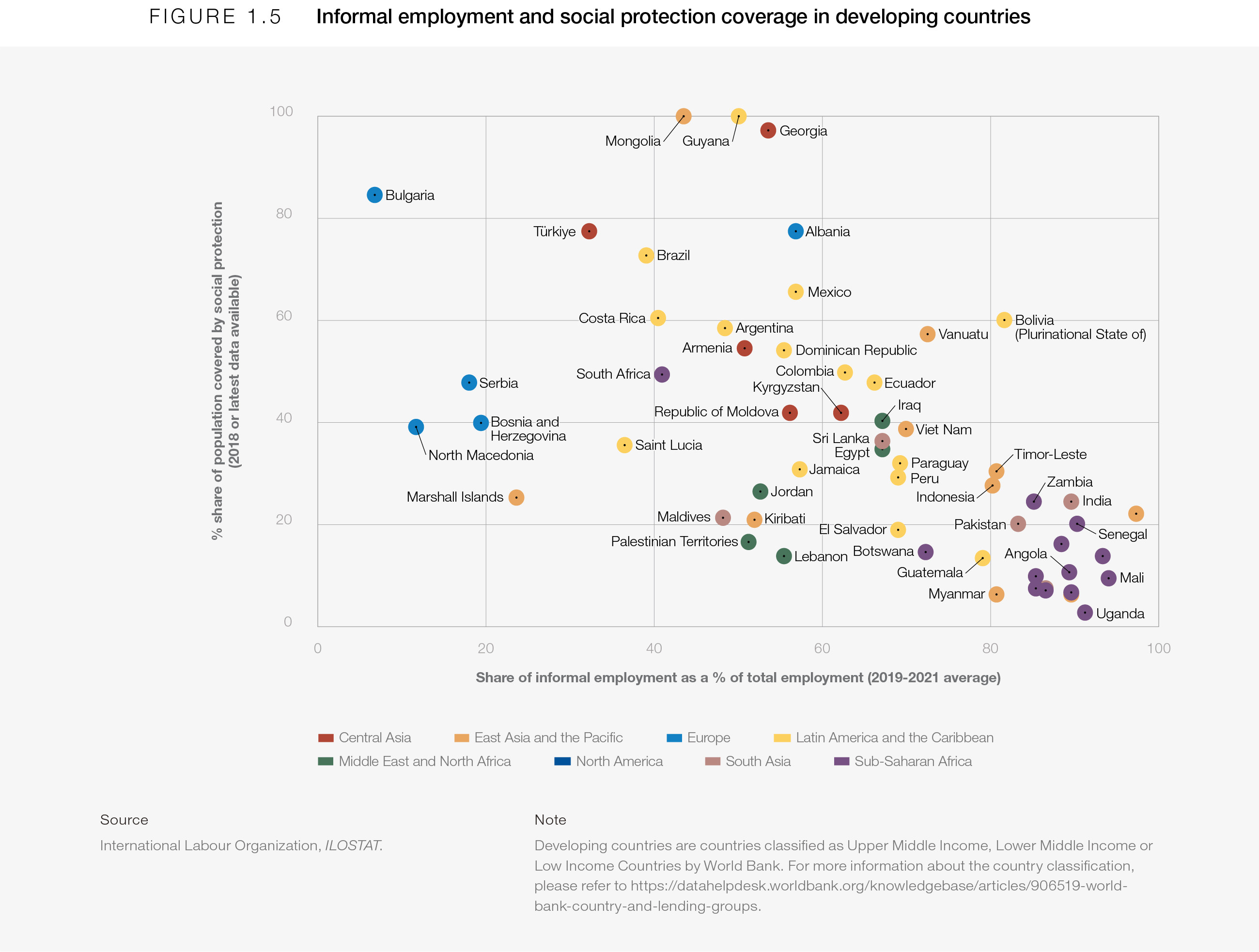
Yet, there remains an urgent need to provide adequate social protection to those not covered by full-time employment contracts (Figure 1.5). Nearly 2 billion workers globally are in informal employment, representing close to 70% of workers in developing and low-income countries, as well as 18% in high income ones.13 Given their susceptibility to economic shocks and working poverty, informal workers represent a crucial labour-market cohort and need better representation in data, broad-based income support in the short term and a longer term shift towards formalization.
Real wages and cost of living
According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), labour income in many developing countries remains below pre-pandemic levels.14 In 2020, the global economy started experiencing inflation levels not seen in almost 40 years.15 With high inflation, the global cost-of-living crisis has hit the most vulnerable hardest.16 According to the ILO, for the first time over the last 15 years, workers’ real wages have declined – by 0.9% in the first half of 2022.17
Across regions, real wage growth was most affected in Northern, Southern and Western Europe; Latin America; Asia Pacific; and North America.18 In Africa, real wages saw a 10.5% drop in 2020 due to the global pandemic.19 However, real wages have continued to increase in 2022 across Asia Pacific, Central and Western Asia and Arab states.20
In line with rising inflation, purchasing power has declined for the most vulnerable, given the higher weight of energy and food in expenditures of the lowest-income households.21 According to recent research by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), rising food and energy prices could push up to 71 million people into poverty, with hot spots in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Balkans and the Caspian Basin.22 This cost-of-living crisis highlights the importance of designing permanent models of social protection for non-standard employment and the informal economy that provide security and support resilience.23
Worker preferences
In this context of diverging labour-market outcomes, issues around the quality of work have come to the fore. This section reviews some of the latest worker preference research to analyse which job attributes are of most importance to workers currently. As a starting point, data shows workers, openness to changing employer. Data on worker preferences from CultureAmp24 and Adecco25 find that more than a quarter (33% and 27% of workers, respectively) do not see themselves at their current company of employment in two years’ time. In line with this, a little under half of workers (42% and 45%, according to CultureAmp and Adecco, respectively) actively explore opportunities at different companies.
Worker surveys at both CultureAmp26 and Randstad27 suggest that salary levels are the main reason workers decide to change their job. 52% of Randstad respondents say they worry about the impact of economic uncertainty on their employment and 61% of respondents to Adecco’s worker-preference survey worry that their salary is not high enough to keep pace with the cost of living given rising rates of inflation.28
Additional data explores the protection and flexibility of employment: 92% of respondents to Randstad’s employee survey29 say job security is important and more than half of these respondents wouldn’t accept a job that didn’t give assurances regarding job security. 83% prioritize flexible hours and 71% prioritize flexible locations.
A fourth theme identified by workers is work-life balance and burnout: 35% of CultureAmp respondents indicate that work-life balance and burnout would be the primary reason to leave their employer. Workers responding to Randstad’s employee survey30 value salary and work-life balance equally, with a 94% share identifying both aspects of employment as important to choosing to work in a particular role.
Data also suggests that diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) at work is particularly important to young workers. According to Manpower,31 68% of Gen Z workers are not satisfied with their organization’s progress in creating a diverse and inclusive work environment, and 56% of Gen Z workers would not accept a role without diverse leadership. Meanwhile, data suggests that fewer women than men are trained.
Lastly, workers across age ranges indicate dissatisfaction about training opportunities. Manpower data32 show that 57% of surveyed employees are pursuing training outside of work, because company training programmes do not teach them relevant skills, advance their career development or help them stay competitive in the labour market. Respondents to Adecco’s survey criticize companies for focusing their efforts too much on managers’ development, skills and rewards. Only 36% of non-managers who responded to Adecco’s survey said that their company is investing effectively in developing their skills, compared to 64% of managers.
Employment shifts across sectors
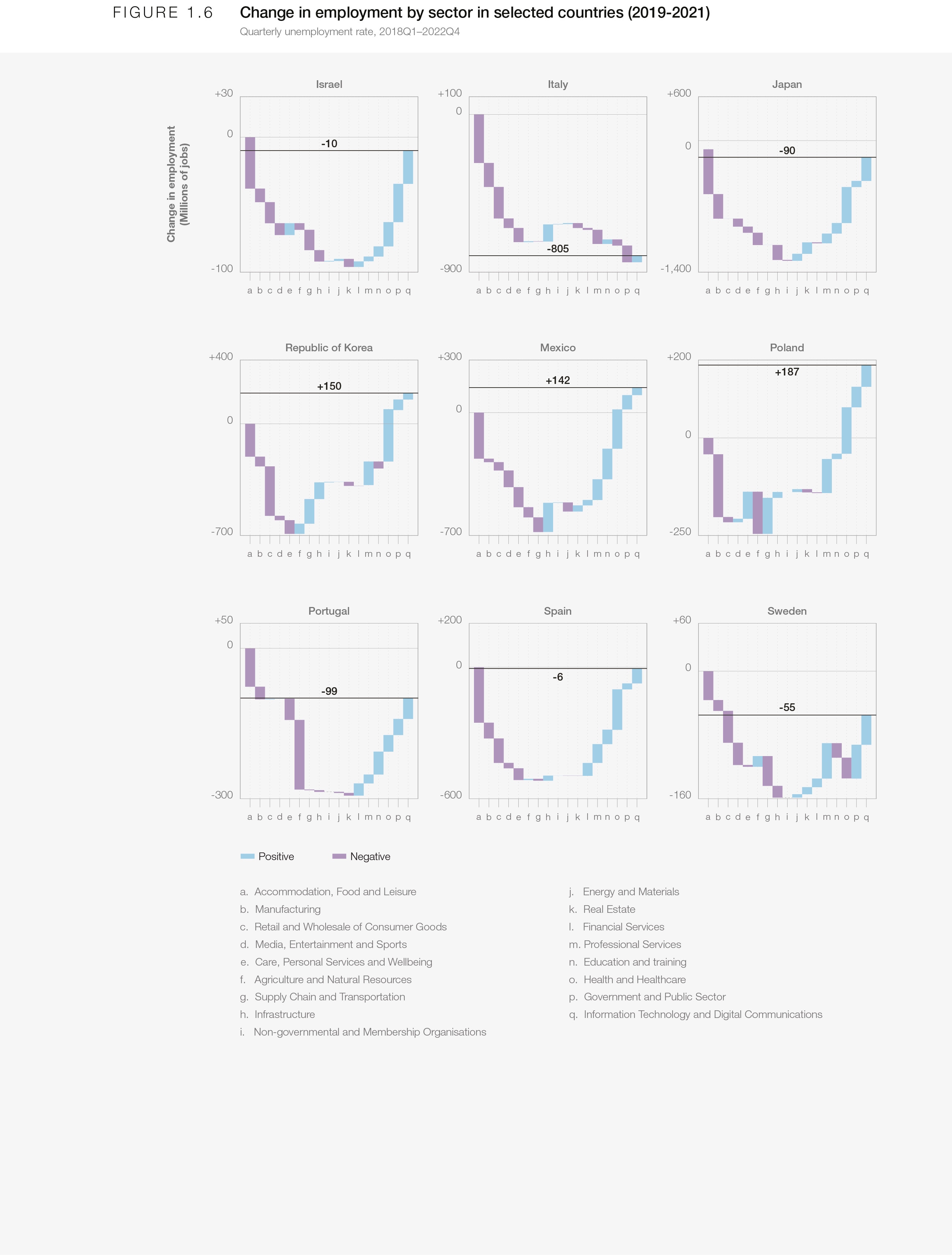
The past two years have witnessed a volatility in the demand and supply of goods and services resulting from lockdowns and supply-chain disruptions. The global economic rebound has reconfigured the sectoral distribution of employment across industries. Figure 6 presents OECD data demonstrating that, while Information Technology and Digital Communications experienced a strong rebound in most countries, the Accommodation, Food and Leisure; Manufacturing and Consumer; and Wholesale and Consumer Goods sectors are experiencing a slower rate of recovery. Since the first quarter of 2019, a majority of countries have experienced employment growth in Professional Services, Education and Training, Health and Healthcare, and Government and Public Sector, but employment in the Supply Chain and Transportation and Media, Entertainment and Sports sectors lags behind 2019 levels.
In addition to the pandemic-induced employment shifts we have seen across sectors during the last few years, generative AI models are likely to continue shaping sectoral shifts in employment. While AI applications are shown to be effective general-purpose technologies,33 the development of general-purpose technologies have previously been hard to predict, which is why regulation needs to be both prompt and adaptable as institutions learn how these technologies can be used.

Through research conducted for the Future of Jobs Report, LinkedIn has identified the fastest growing roles globally over the past four years, shedding further light on the types of jobs employers have been seeking (Box 1.1).
The transformations that labour markets are experiencing have also increased the need for swifter and more efficient job reallocation mechanisms within and across different firms and sectors. The coming years represent a generational opportunity for businesses and policy-makers to embrace a future of work which fosters economic inclusion and opportunity, sets in place policies which will influence not only the rate of growth but its direction, and contribute to shaping more inclusive, sustainable and resilient economies and societies.
The green transition, technological change, supply-chain transformations and changing consumer expectations are all generating demand for new jobs across industries and regions. However, these positive drivers are offset by growing geoeconomic tensions and a cost-of-living crisis.34
The Future of Jobs Survey was conducted in late 2022 and early 2023 bringing together the perspective of 803 companies – collectively employing more than 11.3 million workers – across 27 industry clusters and 45 economies from all world regions. The Survey covers questions of macrotrends and technology trends, their impact on jobs, their impact on skills, and the workforce transformation strategies businesses plan to use.
This chapter analyses findings from the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Survey to explore how businesses expect macrotrends and technology adoption to drive industry transformation and employment.
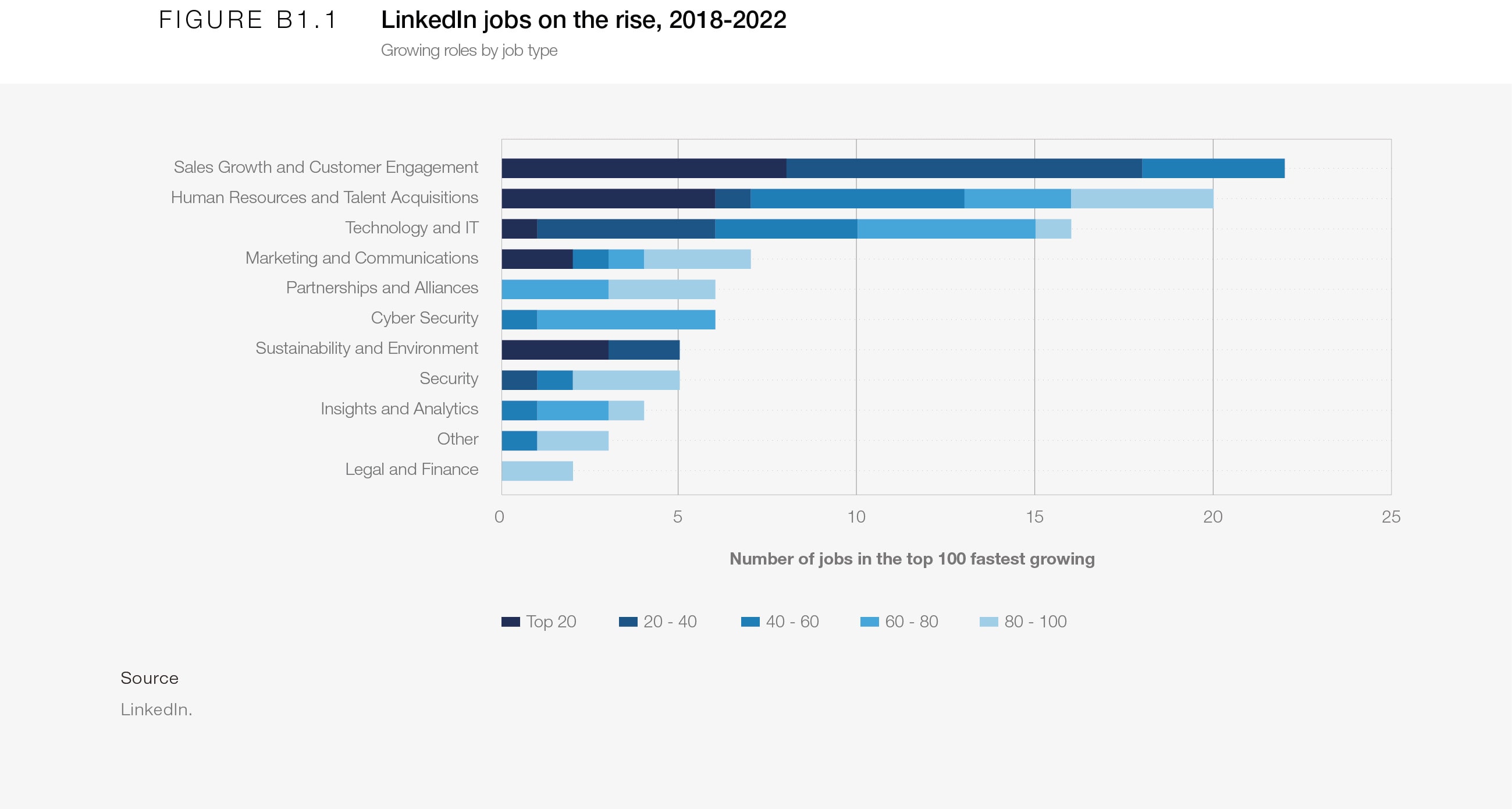
BOX 1.1 The fastest-growing jobs support sales growth and customer engagement, the search for talent, and technology/IT
In collaboration with LinkedIn
Research conducted by LinkedIn for the Future of Jobs Report 2023 describes the 100 roles that have grown fastest, consistently and globally, over the last four years – known as the “Jobs on the Rise”. While ILO and OECD data show which sectors are employing more people, Jobs on the Rise data identifies the specific job types that have experienced significant growth. Figure B.1 organizes the 100 Jobs on the Rise into broad types.
In line with ILO and OECD data on the growth of roles in the Information Technology and Digital Communication sector, Technology and IT related roles make up 16 of the top 100 Jobs on the Rise, the third-highest of all job groupings. Jobs related to Sales Growth and Customer Engagement top the list, with 22 of the 100 roles. With roles such as Sales Development Representatives, Director of Growth, and Customer Success Engineer featuring in this group, this may suggest an increasing focus on broadening customer groups and growth models in a world with increasing digital access and rapid technological advancement (more detail on how increasing digital access and adoption of frontier technologies could transform demand for specific job types is available in Chapter 3). Human Resources and Talent Acquisition roles are the second-most popular roles, and most of these relate to Talent Acquisition and Recruitment, including a specific role for Information Technology Recruitment – perhaps illustrating the increasing difficulty and importance of accessing talent in a generally strong labour market.
Of the groups further down the list, Sustainability and Environment related roles are notable for all being in the top 40, including three of the top 10 roles (Figure B.2). This might suggest the green transition is both a significant and developing labour-market trend, where roles have titles such as “Sustainability Analyst”. Chapter 3 further examines the outlook for roles related to a green transition.