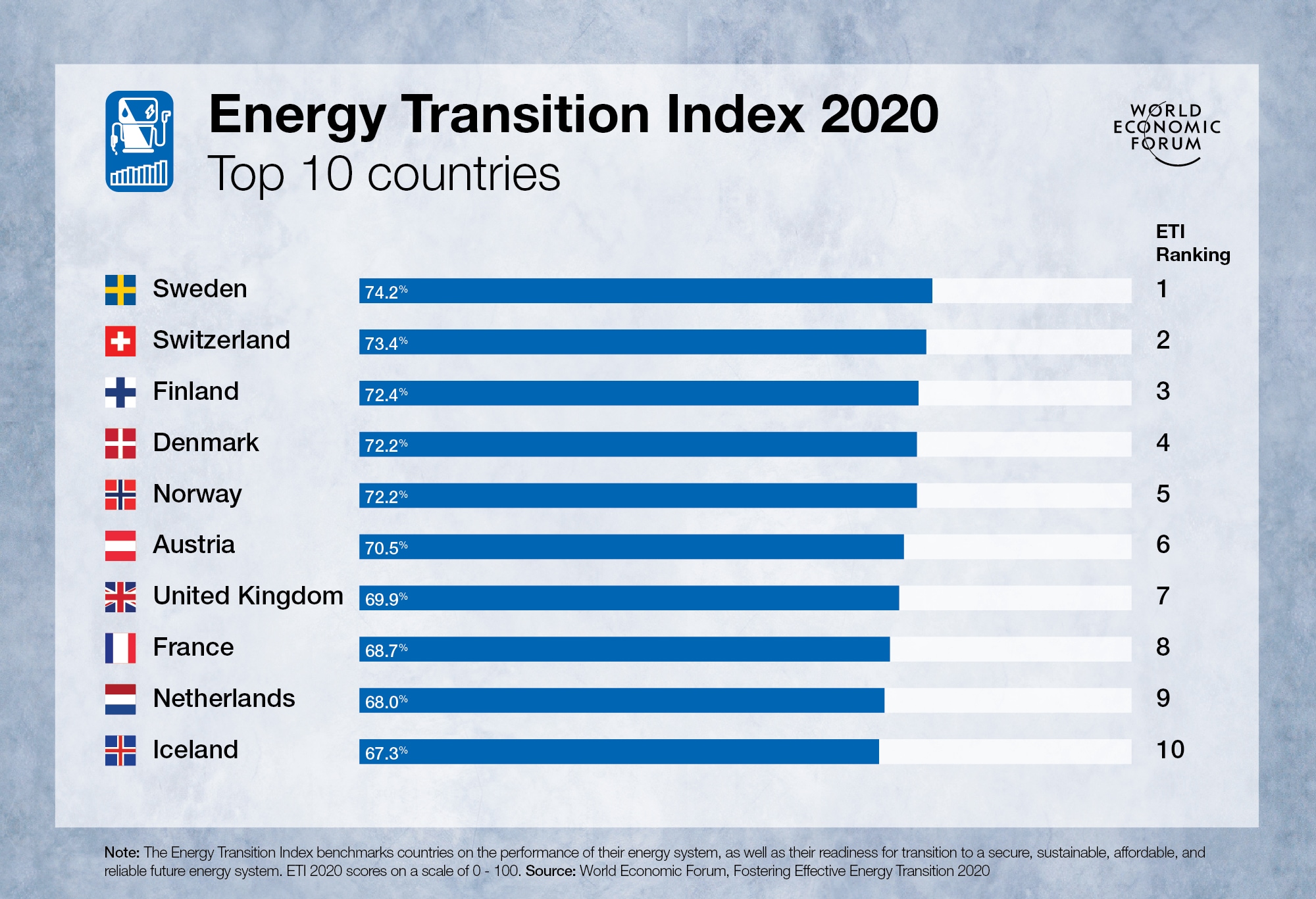
More electric cars are now sold every week than in the whole of 2012

More electric cars are now sold per week than in all of 2012 Image: Unsplash/CHUTTERSNAP

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Automotive and New Mobility
- The global electric car market is growing exponentially.
- Worldwide sales hit 6.6 million in 2021, almost doubling from the previous year.
- But carmakers must overcome challenges such as rising material costs and potential shortages of microchips to maintain market growth.
Think back a decade. In 2012, the nascent electric vehicle (EV) market was starting to gain momentum, with global sales of 130,000 cars. Today, that number of electric cars is sold every week.
While the market for petrol and diesel cars has been dampened by the economic fallout from COVID-19, demand for EVs continues to increase.
Factors like climate change and commitments to reach net-zero are helping drive the global shift to emissions-free motoring.
What's the World Economic Forum doing about the transition to clean energy?
Global sales of electric cars reached 2.2 million in 2019. A year later, while demand for conventional cars contracted, sales of electric cars rose to 3 million, accounting for 4.1% of the world market, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Market momentum has continued, with EV sales more than doubling on the year in 2021 to 6.6 million – accounting for almost 9% of the global market. All net growth in car sales around the world in that year came from electric vehicles.
There are now around 16 million electric cars on the world’s roads, according to an IEA estimate. While operating these vehicles requires the equivalent of Ireland’s total electricity generation, they prevent CO2 exhaust emissions reaching the atmosphere – think of it as removing 16 million oil-fuelled cars from the roads.
Total monthly car sales tend to follow an upward trend as a year unfolds. That said, 2021’s sales in the top-three global markets – China, the US and Europe – were more than 50% higher for each month of the year than in 2020.
In China, the world’s fastest-growing EV market, sales doubled in each month of 2021 compared with a year earlier. Overall in 2021, more electric cars were sold in China than were sold throughout the world in 2020.
Europe experienced 70% market growth, selling 2.3 million fully electric and hybrid electric vehicles in 2021, while US sales more than doubled to beyond half a million vehicles.
The numbers look positive for continued market growth across major markets, but the road ahead for electric vehicles may contain some hidden bumps.
Auto manufacturers must contend with looming supply-side challenges, including increasing bulk material costs. Steel prices doubled in 2021, with aluminium prices spiking by up to 70% and copper up by more than a third.

While these additional costs impacted both conventional and electric vehicle production, EVs also faced specific price challenges associated with battery manufacture, including year-on-year increases for essential materials like lithium carbon (up by 150%), graphite (up by 15%) and nickel (up by 25%). And while there may be a lag before material price hikes hit consumers, the trend is a cause for concern when it comes to market growth.
Another challenge facing the industry is a global shortage of microchips, which has slowed and at times halted production of cars and other products. It’s a shortage that particularly impacts EVs, as their electronic components mean they need 2.3 times more microchips than cars with an internal combustion engine.
Compounding the woes of EV manufacturers, in-demand critical minerals such as lithium and cobalt could be in short supply as early as 2025 unless significant new investment is channelled into expanding production capacity, the IEA says.
Winning the confidence of consumers has been a key part of boosting EV adoption worldwide. The challenge now for car manufacturers and policymakers will be getting new capacity set up to resolve looming supply disruptions, if they are to ensure that electric vehicles continue charging forwards.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Energy TransitionSee all
Jennifer Holmgren
April 23, 2024
Ella Yutong Lin and Kate Whiting
April 23, 2024
Nick Pickens and Julian Kettle
April 22, 2024
Katie Fedosenko and Luciana Gutmann
April 15, 2024
Johnny Wood
April 11, 2024
Alexandre Raffoul and Kai Keller
April 10, 2024