Why the planet needs legally binding obligations to limit climate-mitigation 'free-riders'

Despite the urgency of climate change, global efforts towards climate change mitigation have been ineffectual. Image: Unsplash.
Listen to the article
- Planet Earth is in crisis and global efforts to mitigate climate change have so far fallen short.
- The voluntary nature of international climate agreements means that some countries have become 'free-riders': where one nation receives the benefits of reduced GHG emissions without contributing to the costs.
- This is why we need globally recognized, legally binding obligations to prevent exploitation of the environment.
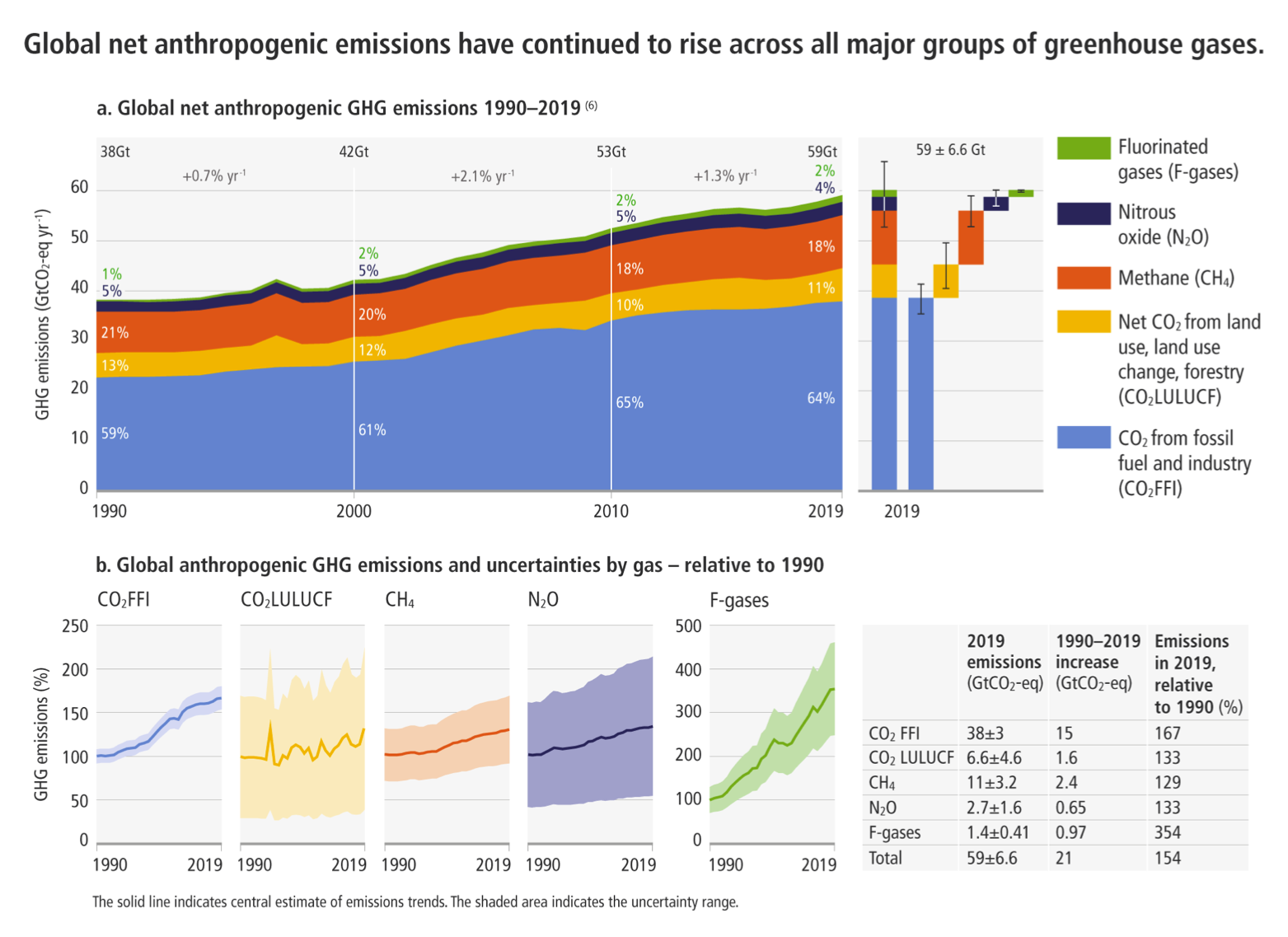
The causes and effects of climate change are global – carbon emissions anywhere in the world endanger people everywhere. As a result, since 1979, climate and weather extremes have caused 2 million deaths and mounting economic losses. Additionally, in the future, climate change is expected to cause 250,000 deaths per year.
However, despite the urgency of climate change, global efforts toward climate change mitigation have been ineffectual. The question is, why? In this piece, we use economic principles to comment on the existing international climate governance architecture and offer reasons behind this ineffective climate action.
Climate change mitigation efforts are lagging behind
The atmosphere is a global common-pool resource – it functions as a sink for greenhouse gases (GHGs). Since the industrial revolution, increased anthropogenic emissions (primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels) have altered the Earth’s energy balance, and have caused planetary warming. Reports show that human activities have warmed the Earth by approximately 1.1°C: compared to the 19th century. In fact, 2021 was one of the hottest years ever recorded.
Consequently, this human-induced warming is a significant contributor to the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events that threatens lives and livelihoods. Some recent examples include severe heatwaves in Australia, the United States and Canada to flooding in Europe and China to extreme droughts in Ethiopia and tropical cyclones in Southeast Asia. However, despite climate change being a pressing concern; global efforts towards climate change mitigation (measures undertaken to avoid and reduce the emission of heat-trapping GHGs) have failed to produce the desired result.
Moreover, between 1995 and 2021, 26 United Nations climate change conferences were organized. They resulted in producing climate treaties like the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement. Nonetheless, the GHG index has increased by 41%, since the 1990s. For the year 2021, “global energy-related carbon dioxide emissions rose by 6%” to 36.3 billion tonnes, their highest ever level.
Why has this happened? The answer lies in economics.
What is the 'free-rider' problem and how does it apply to climate change?
In contemporary economics, public goods possess two characteristics: they are “non-excludable” and “non-rival”. Simply put, they are goods that are available to all, and its enjoyment by one user does not prevent others from using it.
Climate change mitigation (CCM) is a global public good. This is because if India undertakes mitigation efforts to reduce its GHG emissions, it cannot “exclude” China from enjoying the benefits of its effort – irrespective of whether China reciprocates with a similar policy. However, notably, costs are only borne by the country implementing the green policy (for example, India).
Further, this “non-excludable” characteristic of climate change mitigation creates a free-rider problem – an instance where a country receives the benefits of reduced GHG emissions without contributing to the costs. A country implementing a green policy incurs 100% of the cost – either in the form of adopting low carbon technologies or other short-term transition costs for switching to cleaner energy – but receives lesser benefits (in comparison to the costs incurred). Primarily because benefits from climate change mitigation spill beyond national borders due to the global nature of the atmosphere.
This spillover-effect creates strong incentives for a large number of nations to free-ride at the expense of others. Ironically, it motivates them to invest resources in national objectives where benefits do not spill beyond national borders. When a number of countries follow such acts of rational self-interest; it results in a collective disaster – an unsustainable exploitation of the environment. Additionally, it is rather unfortunate that the existing international climate governance architecture has fallen short to address this free-riding syndrome.
The problem with international climate agreements and what needs to change
Under international law, there is no legal mechanism to address the free-riding syndrome – because international agreements are voluntary arrangements. As a result, they lack strong incentives to penalize withdrawal from an agreement or for not meeting the commitments. In the climate context, the result is anarchy.
Powerful countries choose to cooperate only if a proposed new agreement serves its interest. For instance: the United States, a major emitter, did not ratify the Kyoto Protocol on grounds that it was unfair to industrialised nations – resulting in its silent death. Similarly, on the issue of lack of incentives, the current Paris Agreement – which aims to limit global warming to preferably 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels – mostly relies on countries to devise and update pledges (or Nationally Determined Contributions) that have no legally binding obligations.
What’s the World Economic Forum doing about climate change?
The result is, most countries make big pledges at conferences, but most of them lack domestic policy backing. For example, at the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties in Glasgow, UK, China (the world’s largest emitter) pledged to reach carbon neutrality by 2060 but offered almost no detail on how, raising concerns about its viability. No wonder, the world is on track for a 2.7°C warming that will have profound impacts on lives worldwide.
Above all, the current framework lacks teeth to address free-riding because it imposes no sanctions for violating terms. Neither does it have a governing body or an international court to enforce its compliance. In 2020, the US withdrew from the agreement without consequences and later rejoined after 107 days. The proposal of Professor William Nordhaus to set up a climate club model to eliminate free riding – using the right incentives to induce cooperation, could be one step in the right direction to find a solution to the problem. The model shows how a club of nations can price carbon and impose trade sanctions (via uniform percentage tariff) on all non-participating countries to internalize transnational externalities.
The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), designed to prevent carbon leakages is quite similar as it uses trade policy to create the right incentives for climate protection. It certainly is a step in the right direction to achieve net-zero GHG emissions by 2050. However, the Russian invasion of Ukraine will affect the pace of negotiations around CBAM. Thus, immediate structural changes are required to disincentivize acts of rational self-interest to ensure that efforts made by blocs like the European Union don’t go in vain.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Stay up to date:
SDG 13: Climate Action
Forum Stories newsletter
Bringing you weekly curated insights and analysis on the global issues that matter.
More on Climate Action and Waste Reduction See all
Planet in focus: The technologies helping restore balance – and other news to watch in frontier tech
Jeremy Jurgens
November 13, 2025