COVID-19 could kill off handshakes forever

A normal part of social life and business, now cast out. Image: Unsplash/Toa Heftiba

Explore and monitor how COVID-19 is affecting economies, industries and global issues

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
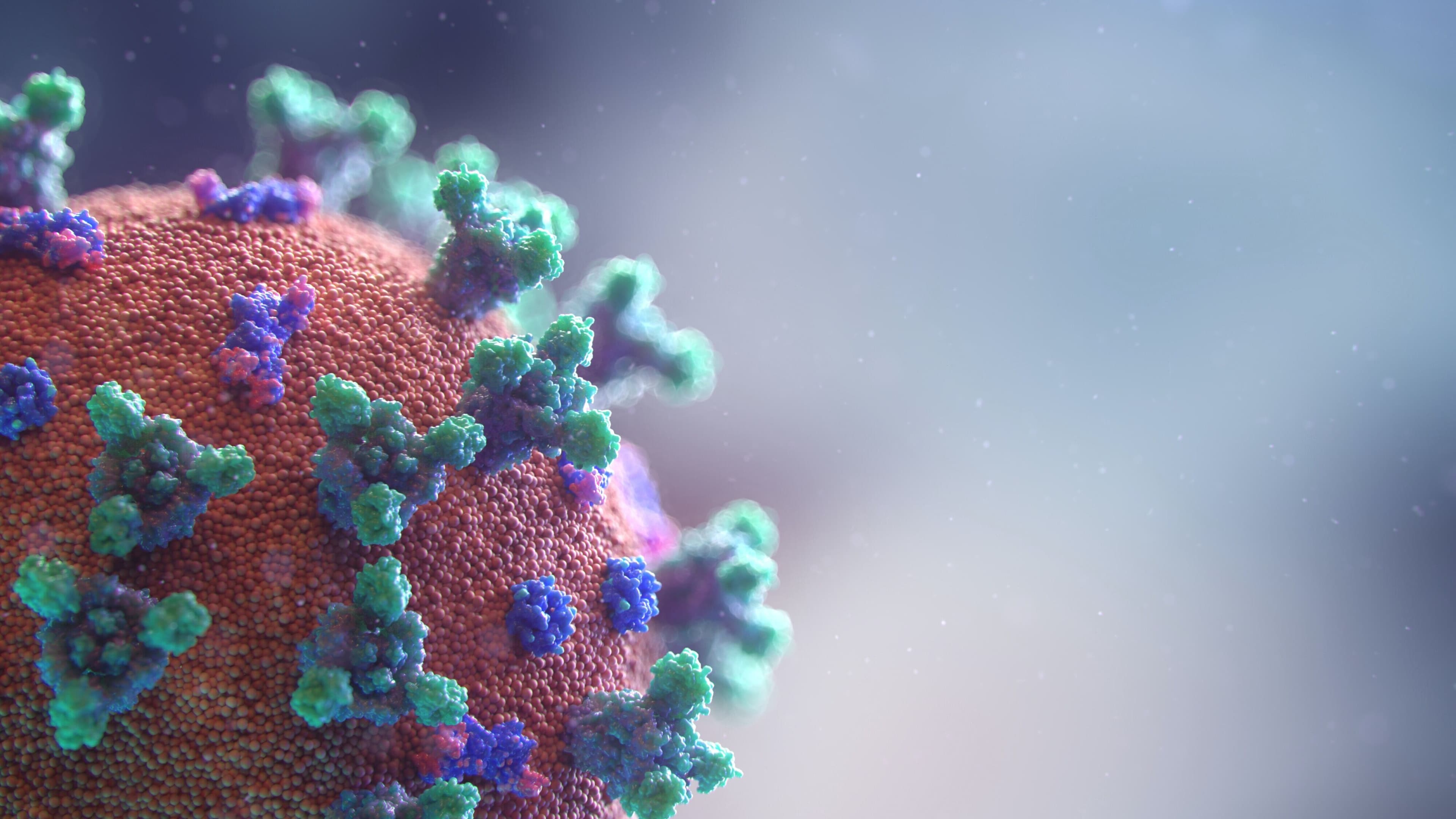
COVID-19
- Handshakes are a big part of society, from business meetings to sporting events.
- Yet our palms carry hundreds of bacteria and viruses - is it time for a change?
- “Every time you touch a surface, you may be picking up up to 50 percent of the organisms on that surface,” says microbiologist Charles Gerba, aka Dr Germ.
It started centuries ago as a symbol of peace, a gesture to prove you weren’t holding a weapon, and over time it became part of almost every social, religious, professional, business and sporting exchange.
But the new coronavirus has forced a rethink of the handshake. No matter how friendly, it is an exchange of potentially infectious microorganisms.
“Hands are like a busy intersection, constantly connecting our microbiome to the microbiomes of other people, places, and things,” a group of scientists wrote in the Journal of Dermatological Science. Hands, they said, are the “critical vector” for transmitting microorganisms including viruses.
But if it is no longer automatically acceptable, what will replace the handshake as a fixture of post-coronavirus social etiquette? A fist or elbow bump? Maybe a traditional Japanese bow or hat doff? How about Spock’s Vulcan salute from Star Trek?
We are social beings. When we meet one another, we press flesh. We take our largest organ, skin, and mash it together with someone else’s - naked. In the middle of the coronavirus it has become clear just how intimate such a gesture is.
The human hand is fecund. We have hundreds of species of bacteria and viruses on our palms.
“Think about it,” says Charles Gerba, a microbiologist and public health researcher at the University of Arizona, who also answers to Dr Germ. “Every time you touch a surface, you may be picking up up to 50 percent of the organisms on that surface.”
Our hands can carry Salmonella, E. coli, norovirus and respiratory infections like adenovirus and hand-foot-mouth disease. And, given how frequently scientists find poop on our fingers and palms, our hygiene habits are far less fastidious than we think.
Bacterial Effervescence
We can’t see any of this with the naked eye.
And so we rely on scientists with agar plates to make visible the arching, spiralling, exploding patterns of bacterial effervescence that show just what our intermingling of fingers risks, something so simple as a handshake rendered in terrifying technicolor.
Scientists can also show us viruses. Those must be studied in animal cells, in a mosaic of tiny semi-circles that scientists often stain purple or red.
The cells are lovely, says Gerba, “and then when they die, they become colourless.”
Gerba studies the movement of viruses. He’ll put a virus on an office doorknob or in a hotel room or someone’s home.
He says it takes just four hours for a virus on an office doorknob to reach half the hands and half the surfaces in an office building, or about 90 percent of the surfaces in someone’s home. A virus in a hotel often moves from room to room and sometimes to nearby conferences.
Gerba says he himself stopped shaking hands during the first SARS outbreak, in 2003. “I always say I have a cold,” he says. “That way I don’t have to shake their hand.”
Top U.S. infectious diseases expert Dr Anthony Fauci sees it the same way since the pandemic hit.
“You don’t ever shake anybody’s hands,” Fauci said this month. “That’s clear.”
Long, hard squeeze
Handshakes have long been a way for humans to signal one another, and part of the ritual of seeking common ground.
“The handshake is what gets photographed at the time of any agreement,” says Dorothy Noyes, a professor of folklore at Ohio State University.
The long, hard squeeze of U.S. President Donald Trump and French President Emmanuel Macron in 2018 was a classic display of two males seeking dominance. Some handshakes, like the bouncing clasp of Chinese President Xi Jinping and Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, take months to negotiate.
Awkward or smooth, handshakes are a hard habit to break, even if we want to.
Minutes after announcing a ban on shaking hands to combat COVID-19, Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte enthusiastically pumped the hand of Jaap Van Dissel, the head of the Dutch Centre for Infectious Disease Control.
“Sorry, sorry! No, that’s not allowed! Let’s do that again,” Rutte said, breaking into a laugh.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on COVID-19See all
Charlotte Edmond
January 8, 2024
Charlotte Edmond
October 11, 2023
Douglas Broom
August 8, 2023
Simon Nicholas Williams
May 9, 2023
Philip Clarke, Jack Pollard and Mara Violato
April 17, 2023