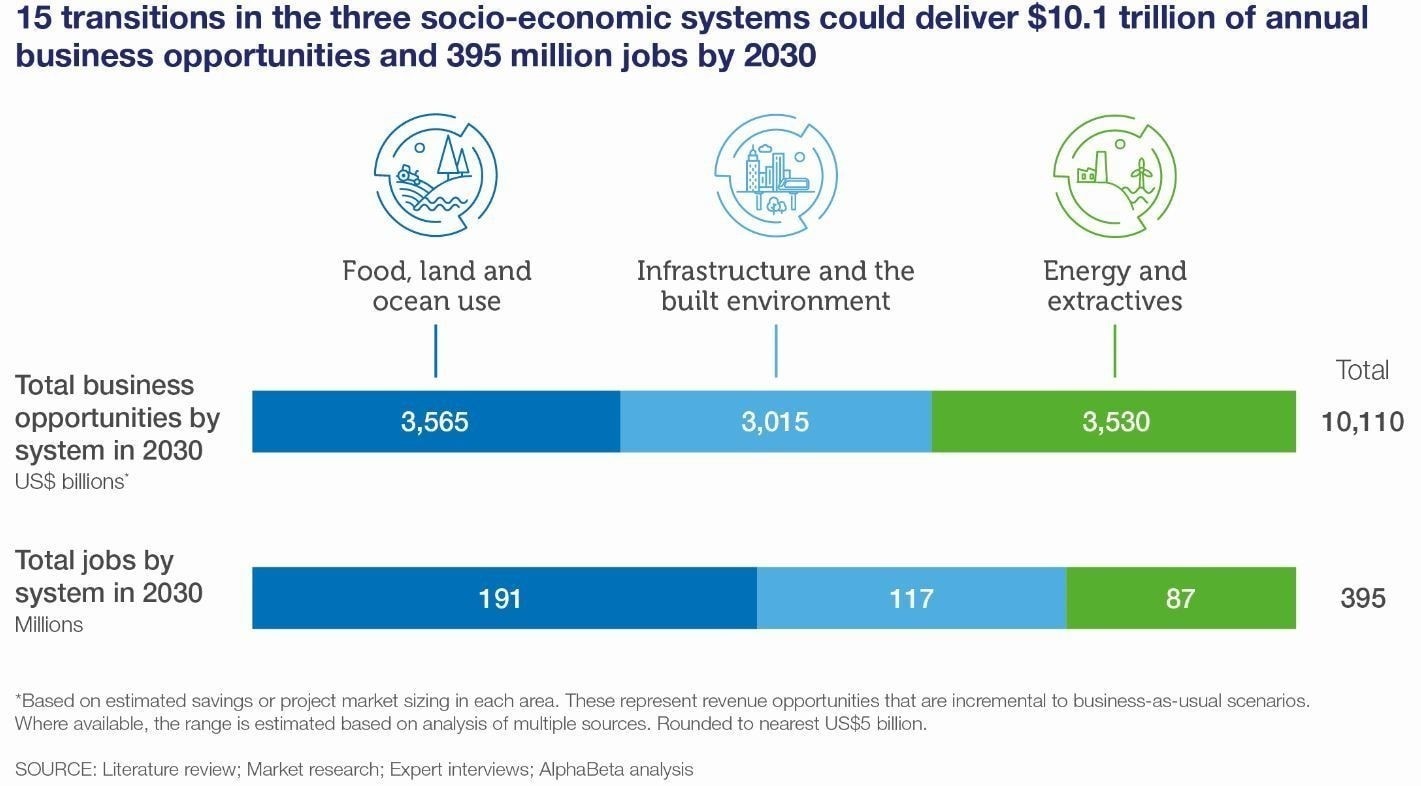
Why are some places more biodiverse?

The rainforests of South America have greater diversity than Central Africa. Why? Image: REUTERS/Nacho Doce
- New research explores why seemingly similar areas have different levels of biodiversity.
- It suggests that high species biodiversity might be linked to how dynamically the continents evolved over time.
- The rainforests of South America, Central Africa and Southeast Asia have very different levels of biodiversity, for example.
Using a new mechanistic model of evolution on Earth, researchers at ETH Zurich can now better explain why the rainforests of Africa are home to fewer species than the tropical forests of South America and Southeast Asia. The key to high species diversity lies in how dynamically the continents have evolved over time.
Tropical rainforests are the most biodiverse habitats on Earth. They are home to a huge number of different plants, animals, fungi and other organisms. These forests are primarily spread over three continents, concentrated in the Amazon Basin in South America, the Congo Basin in Central Africa, and the vast archipelago of Southeast Asia.
One might assume that all tropical rainforests are about equally diverse due to their stable warm and humid climate and their geographical location around the equator – but this is not the case. Compared to South America and Southeast Asia, the number of species in Africa’s humid tropical forests is significantly lower for many groups of organisms.
Palms with few species
A good illustration of this uneven distribution – what researchers refer to as the pantropical diversity disparity (PDD) – is palm trees: of the 2,500 species worldwide, 1,200 occur in the Southeast Asian region and 800 in the tropical forests of South America, but only 66 in African rainforests.
Why this should be so is debated among biodiversity researchers. There is some evidence that the current climate is the cause of the lower species diversity in Africa’s tropical forests. The climate in Africa’s tropical belt is drier and cooler than that in Southeast Asia and South America.
Other evidence suggests that the different environmental and tectonic histories of the three tropical forest regions over tens of millions of years had an impact on the differing levels of biodiversity. Such environmental changes include, for example, the formation of mountains, islands, or arid and desert areas.
However, it is difficult to distinguish between the two factors of current climate and environmental history.
Mountain building brings up diversity
Led by Loïc Pellissier, Professor of Landscape Ecology, researchers at ETH Zurich have now investigated this question with the help of a new computer model that allows them to simulate species diversification over millions of years of evolution. They conclude that the current climate is not the main reason why biodiversity is lower in the rainforests of Africa. Rather, biodiversity has emerged from the dynamics of mountain building and climate change. The results of the historical simulations largely coincide with the patterns of biodiversity distribution observable today.
“Our model confirms that differences in palaeoenvironmental dynamics produced the uneven distribution of biodiversity, rather than current climatic factors,” says Pellissier. “Geological processes as well as global temperature fluctuations determine where and when species emerge or go extinct.”
One factor in particular is crucial to high biodiversity on a continent: geological dynamics. Active plate tectonics promote both the formation of mountains, such as the Andes in South America, and the emergence of archipelagos, as in Southeast Asia. These two processes result in many new ecological niches, which in turn give rise to numerous new species. Africa’s rainforest belt, on the other hand, has had less tectonic activity over the past 110 million years. It is also relatively small because it is bordered by drylands in the north and south, limiting its spread. “Species from humid regions can hardly adapt to the dry conditions of the surrounding drylands,” Pellissier points out.
What is the World Economic Forum doing about nature?
Geologically vibrant continents produce higher biodiversity
The “gen3sis” model developed by ETH researchers was only recently presented in the journal PLoS Biology. It is a mechanistic model in which the primary constraints such as geology and climate are represented together with biological mechanisms and from which biodiversity patterns can materialise. To simulate the emergence of biodiversity, the most important processes to integrate into the model are ecology (i.e. each species has its own limited ecological niche), evolution, speciation and dispersal.
“With these four basic rules, we can simulate the population dynamic of organisms over shifting environmental conditions and offer a very good explanation for how the organisms came about,” Pellissier says.
By building their model on these basic evolutionary mechanisms, the researchers can simulate species diversity without having to input (distribution) data for each individual species. However, the model requires data on the geological dynamics of the continents under consideration, as well as humidity and temperatures from climate reconstructions.
The researchers are now refining the model and running simulations to understand the emergence of biodiversity in other species-rich regions, such as the mountains of western China. The model’s code and the palaeoenvironmental reconstructions are open source. All interested evolutionary and biodiversity researchers can use it to study the formation of biodiversity in different regions of the world.
Reference
Hagen O, Skeels A, Onstein R, Jetz W, Pellissier L. Earth history events shaped the evolution of uneven biodiversity across tropical moist forests. PNAS, Publication date: Oct 1st 2021.
Hagen O, Flück B, Fopp F, Cabral JS, Hartig F, Pontarp M, et al. (2021) gen3sis: A general engine for eco-evolutionary simulations of the processes that shape Earth’s biodiversity. PLoS Biol 19(7): e3001340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001340call_made
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Stay up to date:
Future of the Environment
Forum Stories newsletter
Bringing you weekly curated insights and analysis on the global issues that matter.