Building a pipeline of 50 investible opportunities for a nature-positive economy

Nature-positive economy and investments can benefit both business and the planet. Image: Luís Fernando Torres/Unsplash
- Climate shocks, nature loss and resource constraints are reshaping how businesses across the world operate and do business.
- Investments made to manage these risks can also deliver cost savings, open new revenue sources and lead to more resilient growth.
- The World Economic Forum and Oliver Wyman have identified a pipeline of investible opportunities in critical sectors, which deliver benefits for both companies and the planet.
Climate shocks, nature loss and resource constraints are reshaping the way companies operate around the world. Nature-related risks are already materializing – supply chains are disrupted by floods and droughts, operations are impacted by water stress and nature loss, and companies face environment-related litigation and regulation.
Investments made to manage these risks can, in many cases, also deliver cost savings, open new revenue sources and lead to more resilient growth.
The World Economic Forum, in collaboration with Oliver Wyman, has conducted a systematic analysis of nature-positive business activities that generate economic returns, the full report of which will be published early next year.
From this, we have identified a significant pipeline of investible opportunities in critical sectors, which deliver benefits for both companies and the planet.
These are practical solutions ranging from efficiency improvements to industry-wide transformations, many of which are deployable at scale today. For corporates, they represent not only a pathway to environmental stewardship but also a source of competitive advantage and revenue generation.
Business benefits of transitioning to a nature-positive economy
Transitioning to a nature-positive economy could generate $10.1 trillion in business value by 2030. Companies that act early can reduce costs, strengthen supply chain resilience and access new markets.
Yet hesitation remains. Many firms still perceive investments in nature as costs rather than drivers of growth, and a significant financing gap remains.
This view is rapidly becoming outdated. Across industries, leaders are proving that nature-positive strategies can enhance profitability while safeguarding natural capital – a resource no business can afford to lose.
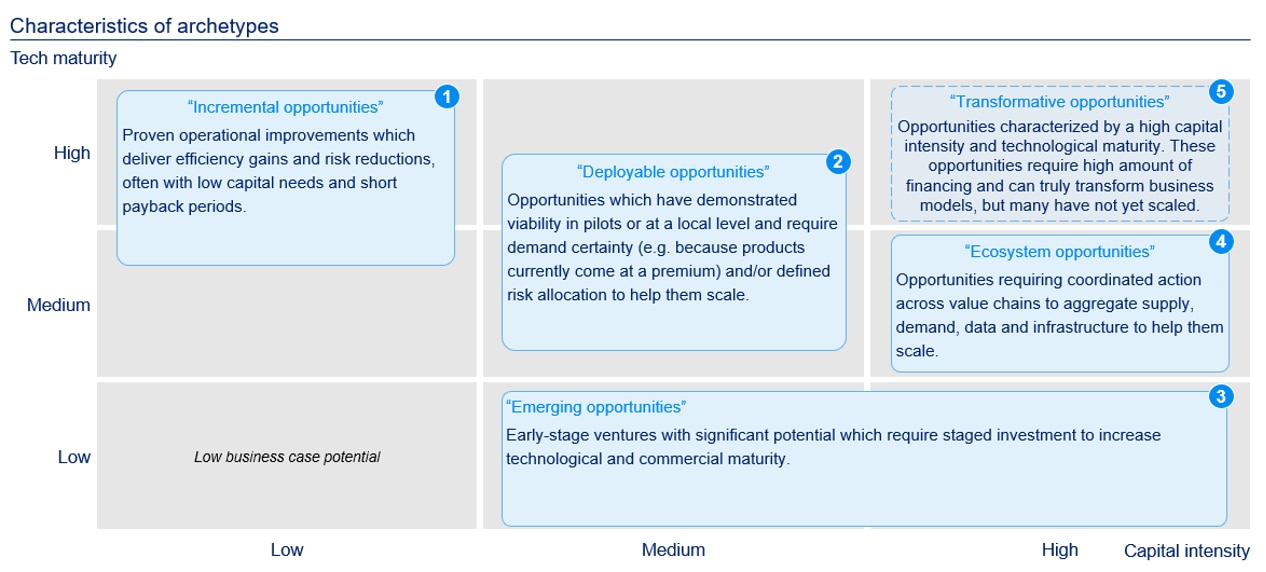
The Forum’s analysis highlights a significant pipeline of investable opportunities across 12 critical sectors – from agriculture and food to cement, mining, energy and technology. These opportunities generally fall into five categories, each offering different pathways to integrate these into business operations:
1. Incremental: efficiency wins hiding in plain sight
Incremental opportunities are the low-hanging fruit. They involve efficiency measures that are relatively inexpensive and could generate significant cost savings while reducing environmental impact.
Mahindra Group, for example, has deployed advanced water management systems across its operations in technology, automotive, agriculture, renewable energy and real estate, improving efficiency and water security while reducing pressure on local freshwater sources.
Such measures can be rolled out quickly, delivering immediate operational savings and building resilience in water-stressed regions.
2. Deployable: scaling proven technologies
Deployable opportunities are technologically viable, available in the market, but not yet commercially mainstream. Holcim is a pioneer in sustainable cement and concrete: the company produces concrete with recycled construction and demolition waste, incorporating from 10% up to 100% recycled content into some products.
By investing early in scaling such technologies, companies can differentiate themselves from peers, meet customer demand for sustainable materials and help build markets that reduce reliance on virgin resources.
Some of these opportunities still rely on high-cost inputs and must be sold at a premium; however, cost curves are going down over time.
3. Emerging: piloting the innovations of tomorrow
Emerging opportunities are early-stage technologies with significant potential. Businesses need to pilot these innovative technologies to help build capabilities for markets of the future. An example of this is the development of innovative irrigation solutions, such as sensor‑guided and artificial intelligence‑assisted scheduling, subsurface drip systems and automated valves.
These technologies improve water use efficiency and reduce run-off in water‑stressed regions. Many of these deployments are still in the pilot phase, yet they represent the frontier of precision water management in agriculture.
4. Ecosystem: collaborating across value chains
Some opportunities require collaboration across sectors. Battery recycling is one such ecosystem play. Across the value chain, BASF is investing in large-scale recycling facilities while start-ups like Cylib and Tozero are innovating in recovery processes.
For businesses, joining these ecosystems ensures access to critical materials, supports circular supply chains and creates new partnerships that spread both costs and benefits. If the rebound effect can be controlled, circularity efforts across value chains have the potential to keep natural resource extraction within planetary boundaries.
Businesses need to partner with peers, suppliers and start-ups to unlock these circular and regenerative value chains.
5. Transformative: reimagining industries
Finally, transformative opportunities involve large-scale, highly mature investments that reshape entire industries. Given their high capital requirements and low risk, financial institutions step in quickly to provide lending and investment through mainstream commercial financial instruments.
While this is the “holy grail” for nature-positive activities, no opportunity quite matches the criteria yet. These require a commitment to systemic change, rethinking business models to thrive in a resource-constrained word. Businesses and financial institutions need to work together to move other opportunities up the curves of maturity and scale to build truly transformative opportunities.
The spectrum enables businesses to start with quick wins while preparing for deeper transformations. Importantly, many of these opportunities fall squarely within value chains, demonstrating that nature-positive strategies can support – not distract from – core business growth.
Why companies must embrace nature-positive strategies
The choice facing companies is clear. Embracing these opportunities strengthens resilience against environmental shocks, creates new revenue streams and builds trust with stakeholders. Ignoring them risks higher costs, stranded assets and lost competitiveness.
How the Forum helps leaders align climate action with nature-positive growth
The tools and technologies are already here. What is needed is corporate leadership: investing in incremental solutions today, deploying new approaches tomorrow, and investing in transformative change for the long term.
By integrating nature-positive investment opportunities into their strategies, companies can help accelerate the transition to a nature-positive economy – one that delivers growth, resilience and a thriving planet.
The full report on 50 investible opportunities as part of the Nature Positive Transitions report series will be available in Spring 2026. For more information, please visit Nature Positive Transitions.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Stay up to date:
Future of the Environment
Related topics:
Forum Stories newsletter
Bringing you weekly curated insights and analysis on the global issues that matter.
More on Nature and BiodiversitySee all
Jack Hurd and Sir Andrew Steer
February 17, 2026






