Climate inaction is costing lives, and other health stories
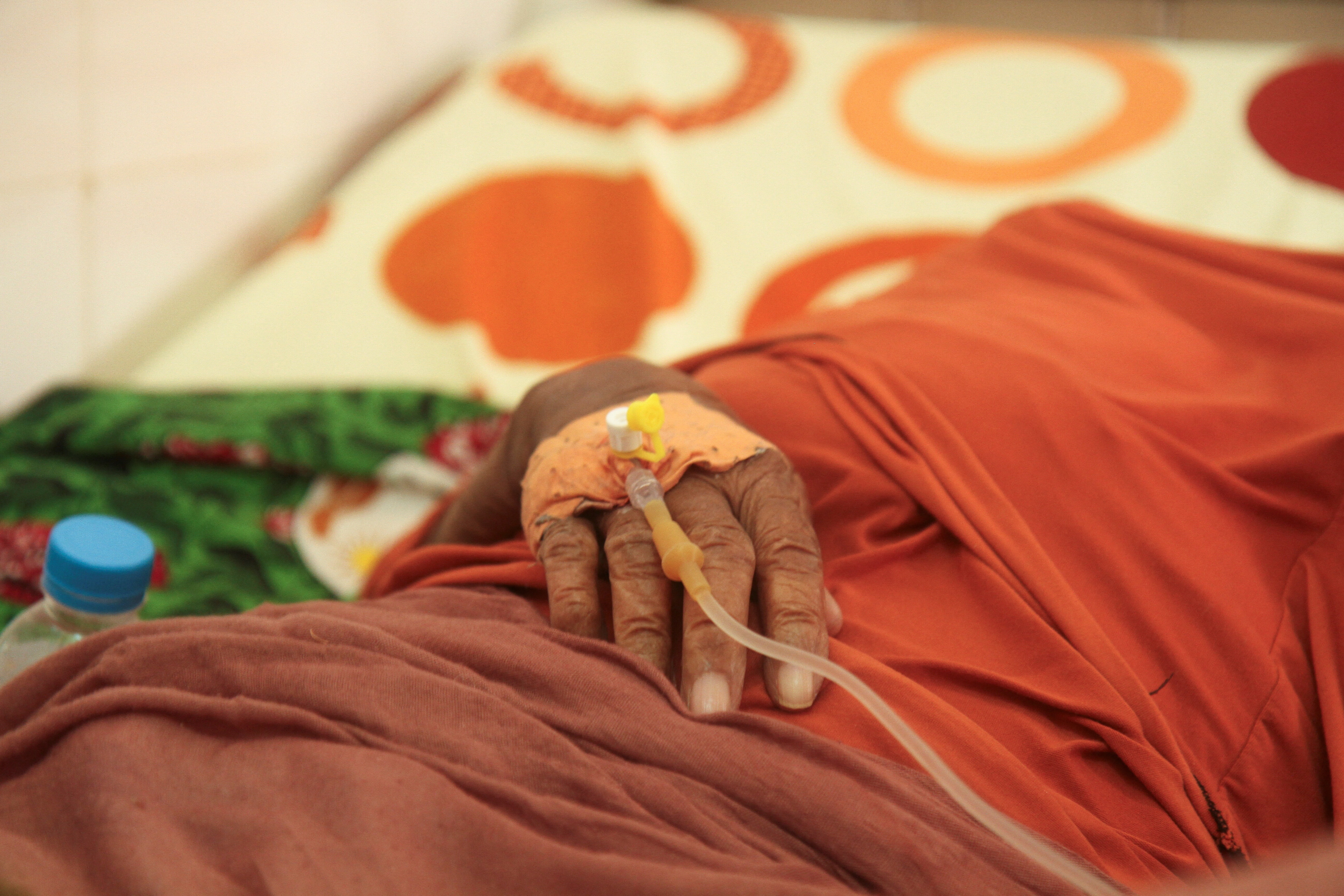

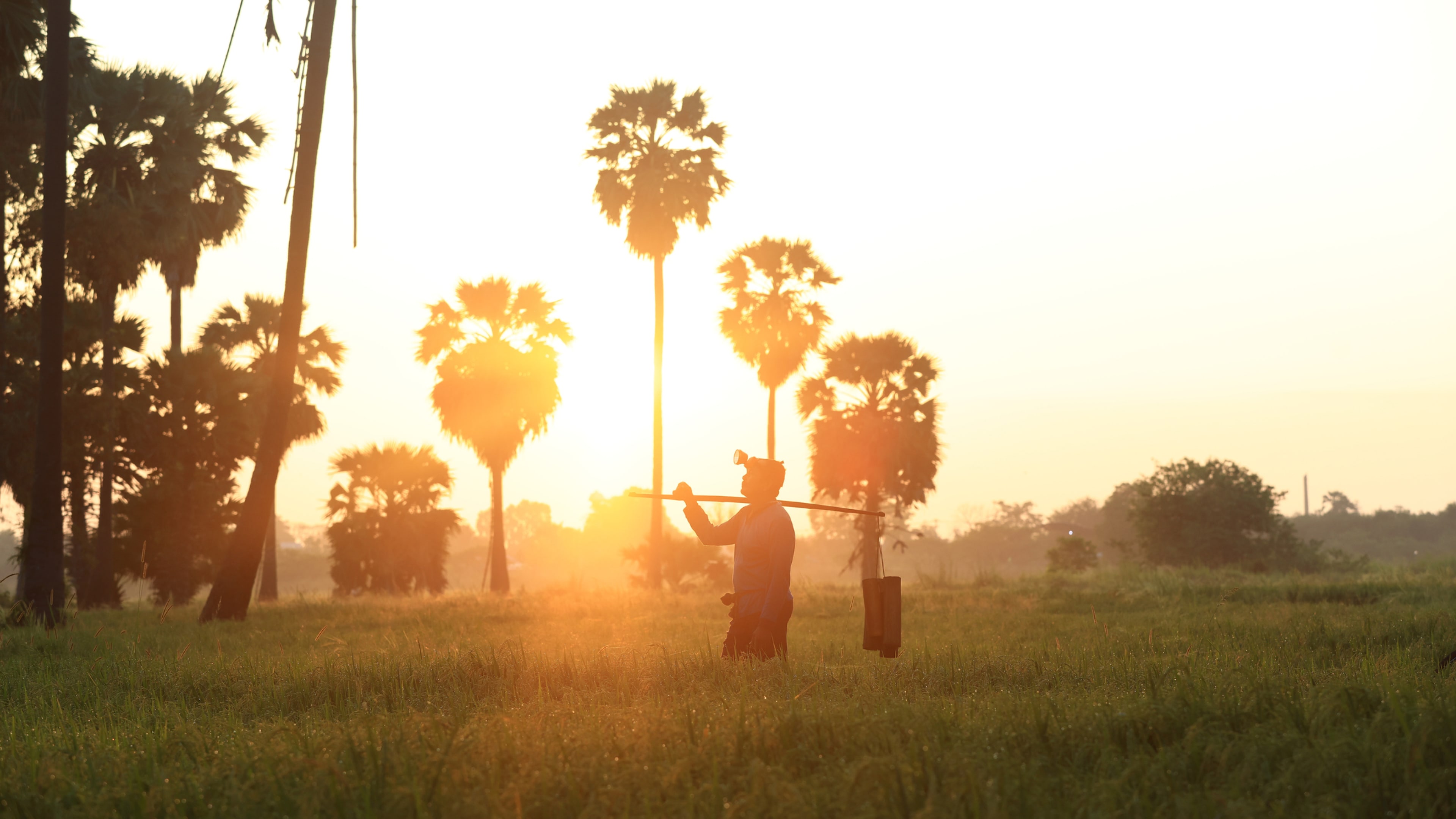
The number of heat-related deaths is rising each year, highlighting a growing public health concern. Image: REUTERS/ Mahamadou Hamidou
Shyam Bishen
Head, Centre for Health and Healthcare; Member of the Executive Committee, World Economic Forum- This global round-up brings you health stories from the past fortnight.
- Top health news: The human cost of climate inaction; Mpox cases rise in Europe; Study suggests daily walk time to improve heart health.
1. Climate inaction is costing millions of lives every year, warns report
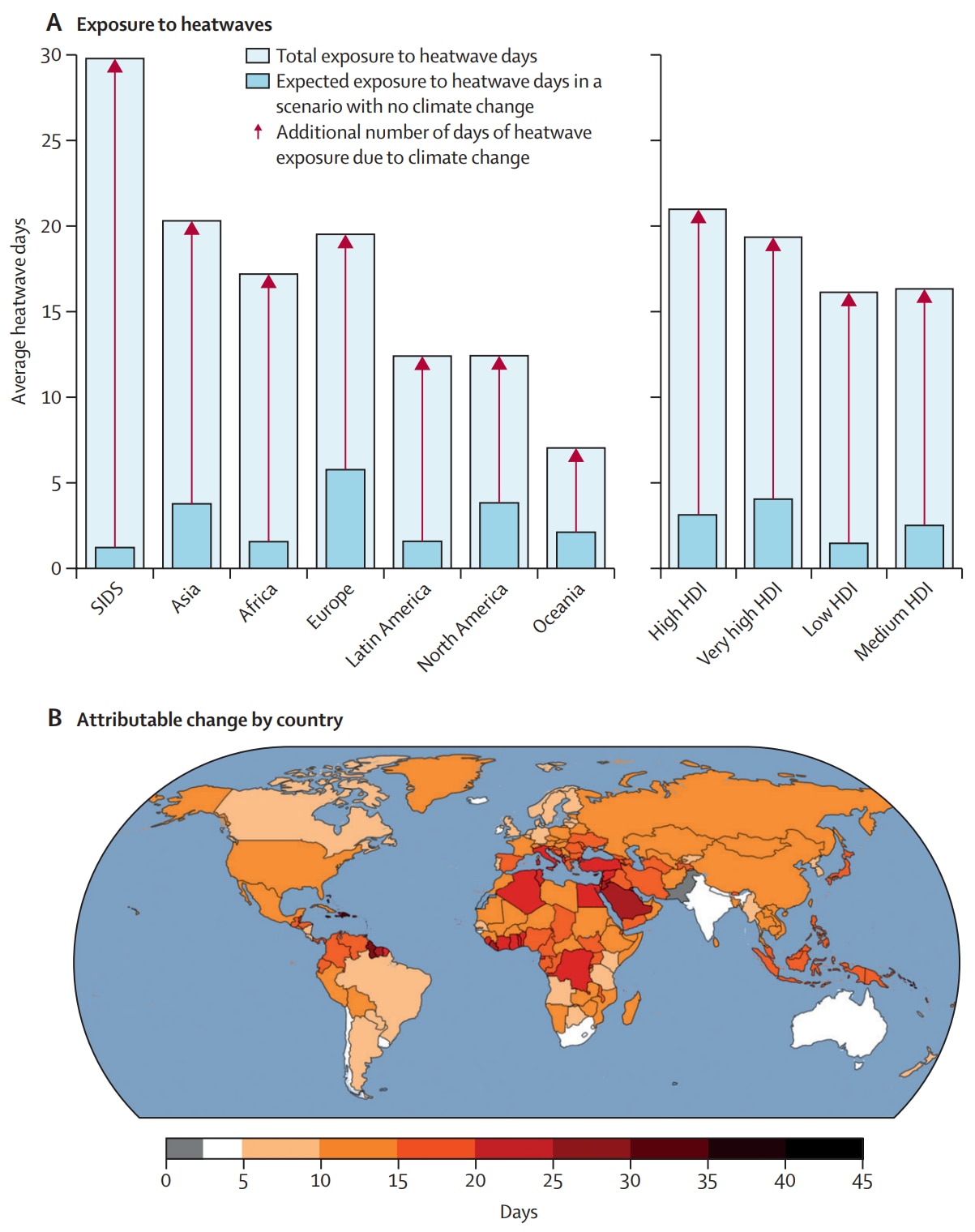
Rising temperatures have pushed 12 of 20 key indicators tracking health threats related to climate change to record levels in the past year, according to the 2025 Lancet Countdown report.
The findings explore how climate inaction is costing lives, straining health systems and undermining economies.
Higher temperatures have led to a 63% increase in heat-related deaths since the 1990s, with an estimated 546,000 average annual deaths from 2012 to 2021, meaning one person dies every minute from extreme heat.
The average person was exposed to 16 days of dangerous heat in 2024 that would not have been expected without climate change, as the graphic below explores.
Other key findings include:
- 124 million people faced moderate or severe food insecurity in 2023 due to droughts and heatwaves.
- 640 billion labour hours were lost in 2024, with productivity losses equivalent to $1.09 trillion.
- $261 billion total costs of heat-related deaths among older adults.
"The climate crisis is a health crisis. Every fraction of a degree of warming costs lives and livelihoods," said Dr Jeremy Farrar, Assistant Director-General at the World Health Organization (WHO). Although the health impacts of the climate crisis are wide-reaching and devastating, climate action also represents a great opportunity: "Cleaner air, healthier diets, and resilient health systems can save millions of lives now and protect current and future generations."
The World Economic Forum's Centre for Health and Healthcare has a wide range of research and analysis on the impacts of the climate crisis on health and healthcare systems, as well as how we can build resilience and adapt to this escalating crisis, which you can explore below.
2. Mpox on the rise across Europe
A strain of monkeypox (Mpox) called 'clade Ib' is spreading across some European countries, a report from the UK's Health Security Agency has found.
Small numbers of cases have been reported by authorities in Spain, Italy, Portugal, England and the Netherlands, as well as the US.
What is Mpox? It is classified as a zoonosis, which means a disease that is transmitted between humans and animals. Mpox usually presents with a fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes. Early stages (1-3 days) involve headache and backache, sore muscles and lack of energy. Individuals with the infection will also often develop a rash 1-5 days from the onset of symptoms, starting as raised spots before turning into fluid-filled blisters, which ultimately turn into scabs and fall off.
The report has upgraded the risk of clade Ib being imported into the UK through travel from medium to high. It says onwards spread 'is likely to be controlled to some degree' by the existing vaccination programme for gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (GBMSM), a group within which the virus has spread rapidly.
Health officials are encouraging members in or close to the GBMSM community to get vaccinated to protect themselves and others.
With Winter Pride season soon upon us across Europe, those travelling to these events would be wise to get vaccinated, at least once, if not twice.
”3. News in brief: Health stories from around the world
Daily exercise: One longer walk per day is better for your heart than lots of shorter walks, research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine has found. It recommends walking for at least 15 minutes without stopping, which equates to around 1,500 steps. The study looked at 33,560 adults aged between 40-79 in the UK who walked fewer than 8,000 steps per day. They were grouped by the length of their daily walks and their health was then tracked over an eight-year period. Much research has been conducted into step counts, such as the recent findings of the study in the chart below, which recommends 7,000 steps per day to reduce your risk of serious health outcomes.
Blood test for 50 cancers: The 'Galleri' blood test can check for more than 50 types of cancer, which could help speed up diagnoses, the BBC reports. More than half of the cancers found in a trial of 25,000 adults in North America were detected at an early stage, where they are easier to treat.
New antivenom: A single antivenom has been discovered that can protect against 17 different snakebites, a study published in Nature has found. When administered to mice, the treatment protected against toxins from 17 different African snake species and reduced skin damage. With around 300,000 snakebites occurring each year in sub-Saharan Africa, this discovery could have a significant impact on the region.
World's smallest 3D bioprinter could transform surgeries: The device has a 2.7-millimetre-wide print head at the end of a long, flexible arm that could assist physicians by delivering healing hydrogels into a patient's body during surgery. "Bioprinting typically addresses skin defects from the outside. Reaching a defect internally has been a challenge in the field," says Ibrahim Ozbolat, a biomedical engineer at Pennsylvania State University.
NHS expands use of AI to spot liver disease: A programme in Somerset used AI to analyze the blood of 700,000 people over the age of 18 for signs of liver disease, successfully identifying about 700 patients with problems. This will now be rolled out across the rest of the south-west of England.
Contaminated animal meat linked to urinary tract infections (UTIs): One in five UTIs was associated with contaminated poultry and meat, in a study involving 23,483 subjects with UTIs in eight counties in Southern California. Chicken and turkey were the most closely associated with UTIs, pork was next-highest and then beef. The research suggests that animal foods may be an under-reported source of UTIs.
4. More on health from Forum Stories
Unlocking alternatives to antibiotics: Recently, one emerging solution to fight superbugs just took a big step forward: phage therapy. Bacteriophages, or phages, are bacteria's natural predators responsible for maintaining the balance of bacterial populations. They are the most abundant biological entities on Earth and generally 10-100 times smaller than bacterial cells. Typically, one phage is effective against one or a few bacterial strains. Alexandros Pantalis, CEO of Phagos, looks at how a regulatory shift is unlocking alternatives to antibiotics in the fight against superbugs.
Tackling breast cancer: Women are dying at an increasing rate from breast cancer, which continues to be one of the most common cancers worldwide and the leading cause of cancer death among women. As we mark Breast Cancer Awareness Month, it is vital to acknowledge the growing global impact of breast cancer as an urgent global health concern. Despite advances in science and screening, there is so much more that governments, healthcare systems and providers can do to ensure more women get access to timely detection, diagnosis and the treatment they deserve. In fact, the WHO estimates that if current trends continue, there will be 3.2 million new breast cancer cases and more than one million deaths by 2050. AstraZeneca's Naveena Nekkalapudi looks at what needs to be done to reduce breast cancer deaths globally in this article.
AI meets nutrition: Malnutrition and diet-related diseases are costing the world over $8 trillion each year. AI can change this. By combining data, genetics and personalized nutrition, we can prevent chronic illness, cut healthcare costs and strengthen productivity, says Mariam Adebayo. The goal is not just innovation, but equity – ensuring AI-powered nutrition is ethical, accessible and affordable for everyone. Learn more in this article.
How the Forum helps leaders strengthen health systems through collaboration
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Forum Stories newsletter
Bringing you weekly curated insights and analysis on the global issues that matter.
More on Health and Healthcare SystemsSee all
Priya Abani
February 18, 2026