Which US state generates the most wind power? There's a clear winner

Wind power makes up 8.4% of US electricity generation. Image: Unsplash/rabih shasha

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
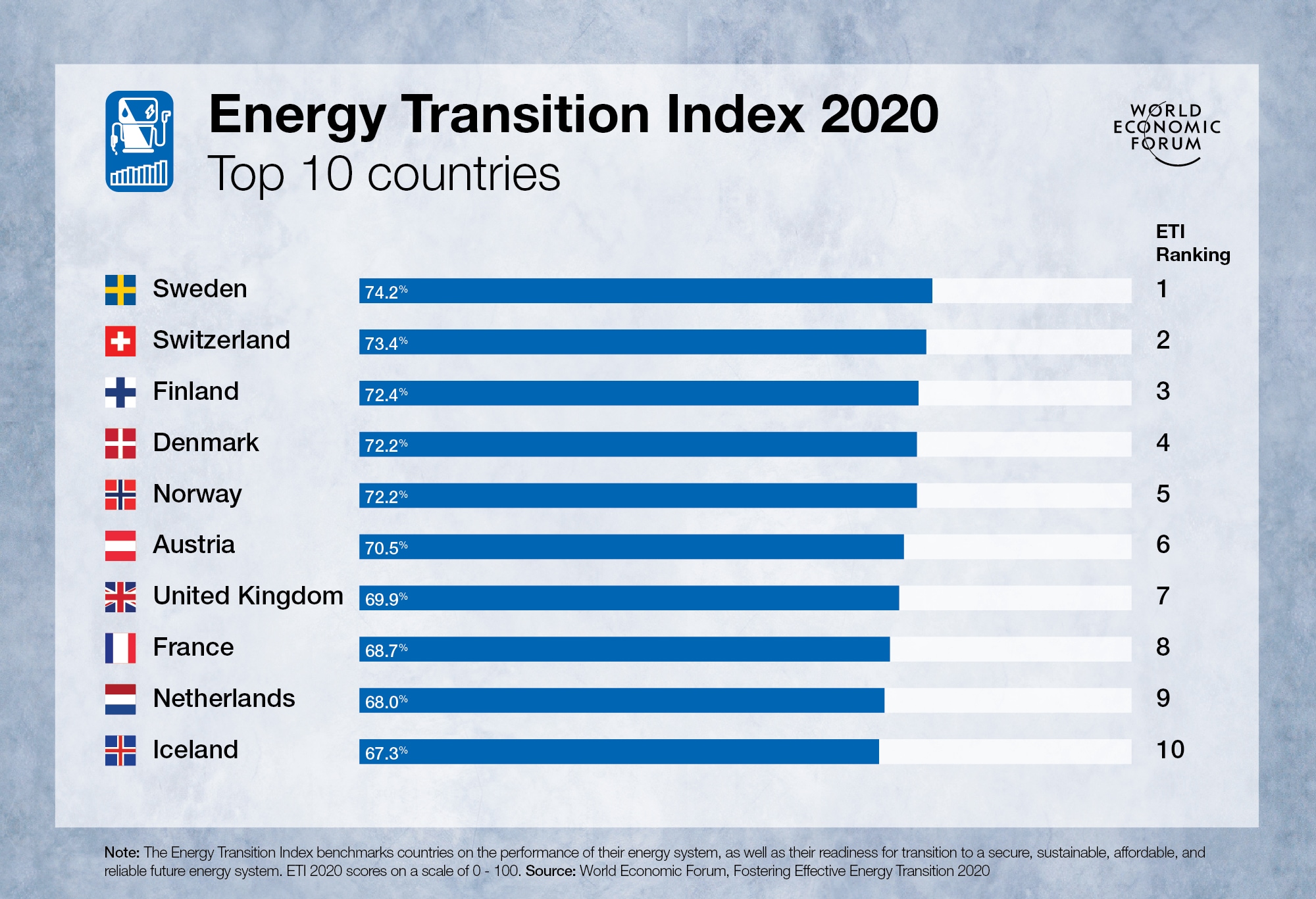
Energy Transition
- Wind power is the largest source of renewable energy in the US, generating nearly half of the total.
- Texas produces far more than any other state, followed by Iowa, Oklahoma and Kansas.
- Just 10 states have no wind power capacity, all in the southeast.
- Record-breaking turbine installations in 2020 and 2021 increased US wind energy generation by 30%.
Mapping U.S. wind energy by state
Wind power is the most productive renewable energy source in the U.S., generating nearly half of America’s renewable energy.
But wind doesn’t blow fairly across the nation, so which states are contributing the most to U.S. wind energy generation?
This map uses data from the EIA to show how much wind electricity different U.S. states generate, and breaks down wind’s share of total electricity generation in top wind power producing states.
Wind power generation by state compared
America’s wind energy generating states are all primarily located in the Central and Midwest regions of the nation, where wind speeds are highest and most consistent.
Texas is the runaway leader in wind, generating over 92 Terawatt-hours of electricity during a year, more than the next three top states (Iowa, Oklahoma, and Kansas) combined. While Texas is the top generator in terms of wind-powered electricity, wind only makes up 20% of the state’s total electricity generation.
Meanwhile, wind makes up a much larger share of net electricity generation in states like Iowa (58%), Oklahoma (35%), and Kansas (43%). For both Iowa and Kansas, wind is the primary energy source of in-state electricity generation after overtaking coal in 2019.
The U.S. also has 10 states with no wind power generating facilities, all primarily located in the Southeast region.
How does wind energy work?
Humans have been harnessing wind power for millennia, with windmills originally relying on wind to pump water or mill flour.
Today’s wind turbines work similarly, with their large blades generating electricity as wind causes them to rotate. As these blades are pushed by the wind, a connected internal shaft that is attached to an electric generator also turns and generates electricity.
Wind power is one of the safest sources of energy and relies on one key factor: wind speeds. When analyzing minimum wind speeds for economic viability in a given location, the following annual average wind speeds are needed:
Small wind turbines: Minimum of 4 meters per second (9 miles per hour)
Utility-scale wind turbines: Minimum of 5.8 meters per second (13 miles per hour)
Unsurprisingly, the majority of America’s onshore wind turbine infrastructure is located in the middle of the nation, where wind speeds are highest.
Growing America’s wind turbine capacity
While wind energy only made up 0.2% of U.S. electricity generating capacity in 1990, it is now essential for the clean energy transition. Today, wind power makes up more than 10% of U.S. electricity generating capacity, and this share is set to continue growing.
Record-breaking wind turbine installations in 2020 and 2021, primarily in the Central and Midwest regions, have increased U.S. wind energy generation by 30% to 135.1 GW.
In 2020, the U.S. increased wind turbine capacity by 14.2 gigawatts, followed by another 17.1 gigawatts in 2021. This year is set to see another 7.6 GW come online, with around half of 2022’s added capacity located in Texas.
After two years of record-breaking wind turbine installations, 2021’s expiration of the U.S. production tax credit is likely to dampen the rate of future installations.
What's the World Economic Forum doing about the transition to clean energy?
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Energy TransitionSee all
Tarek Sultan
April 24, 2024
Jennifer Holmgren
April 23, 2024
Ella Yutong Lin and Kate Whiting
April 23, 2024
Nick Pickens and Julian Kettle
April 22, 2024
Katie Fedosenko and Luciana Gutmann
April 15, 2024
Johnny Wood
April 11, 2024