5 charts that reveal the state of the global arms trade

Saudi helicopters in formation – the country has become the world's biggest importer of military hardware Image: REUTERS/Ahmad Masood

Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
International Security
This article is part of the World Economic Forum's Geostrategy platform
The volume of international transfers of major arms in 2014–18 was 7.8% higher than in 2009–13 and 23% higher than in 2004–2008, according to new data on arms transfers published by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
The five largest exporters in 2014–18 were the United States, Russia, France, Germany and China. Together, they accounted for 75% of the total volume of arms exports in 2014–18. The flow of arms increased to the Middle East between 2009–13 and 2014–18, while there was a decrease in flows to all other regions.

The gap between the USA and other arms exporters widens
US arms exports grew by 29% between 2009–13 and 2014–18, and the US share of total global exports rose from 30% to 36%. The gap between the top two arms-exporting states also increased: US exports of major arms were 75% higher than Russia’s in 2014–18, while they were only 12% higher in 2009–13. More than half (52%) of US arms exports went to the Middle East in 2014–18.
"The USA has further solidified its position as the world’s leading arms supplier," says Dr Aude Fleurant, Director of the SIPRI Arms and Military Expenditure Programme. "The USA exported arms to at least 98 countries in the past five years; these deliveries often included advanced weapons such as combat aircraft, short-range cruise and ballistic missiles, and large numbers of guided bombs."
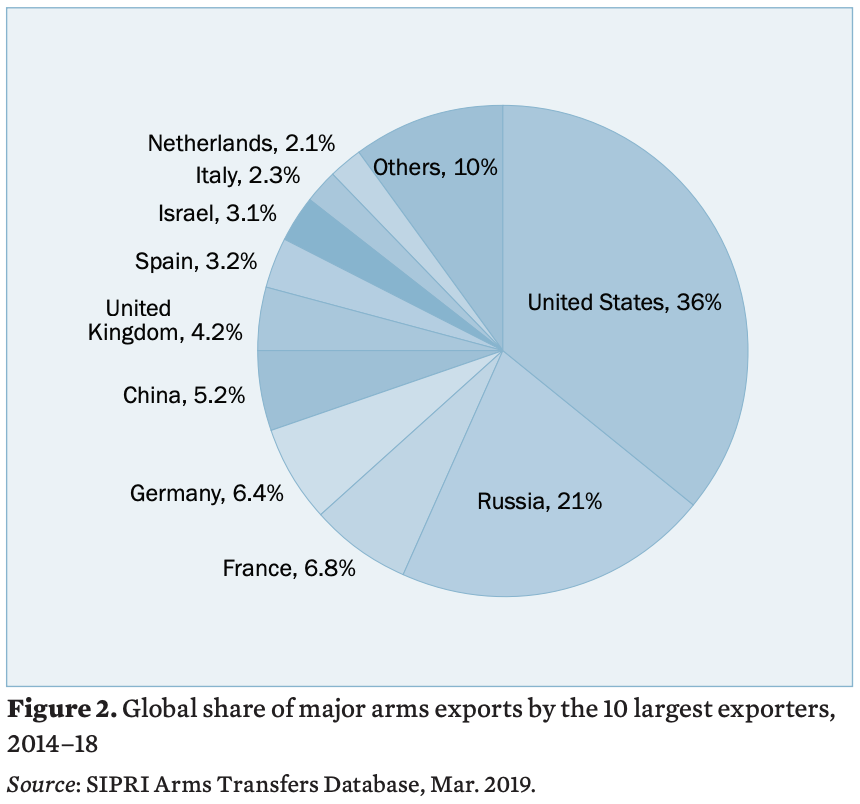
Arms exports by Russia decreased by 17% between 2009–13 and 2014–18, in particular due to the reduction in arms imports by India and Venezuela.
Between 2009–13 and 2014–18 France increased its arms exports by 43% and Germany by 13% The combined arms exports of European Union member states accounted for 27% of global arms exports in 2014–18.

A small number of countries outside Europe and North America are large arms exporters. China was the fifth largest arms exporter in 2014–18. Whereas Chinese arms exports rose by 195% between 2004–2008 and 2009–13, they increased by only 2.7% between 2009–13 and 2014–18. Israeli, South Korean and Turkish arms exports increased substantially—60%, 94% and 170%, respectively—between 2009–13 and 2014–18.
Middle Eastern arms imports almost double in the past five years
Arms imports by states in the Middle East increased by 87% between 2009–13 and 2014–18 and accounted for 35% of global arms imports in 2014–18. Saudi Arabia became the world’s largest arms importer in 2014–18, with an increase of 192% compared with 2009–13. Arms imports by Egypt, the third largest arms importer in 2014–18, tripled (206%) between 2009–13 and 2014–18. Arms imports by Israel (354%), Qatar (225%) and Iraq (139%) also rose between 2009–13 and 2014–18. However, Syria’s arms imports fell by 87%.
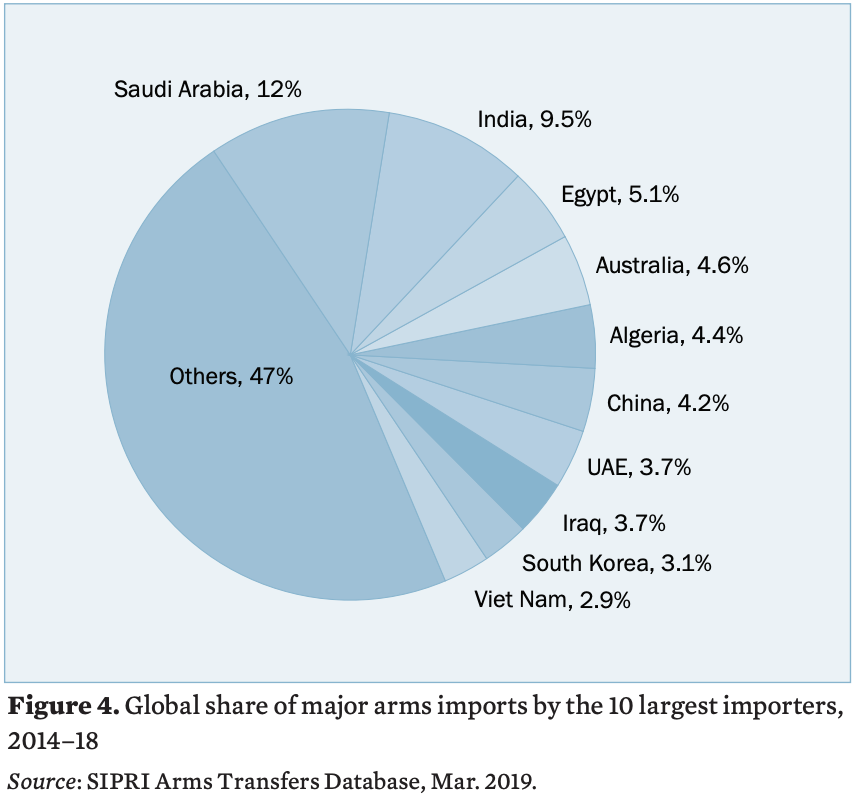
"Weapons from the USA, the United Kingdom and France are in high demand in the Gulf region, where conflicts and tensions are rife," says Pieter D. Wezeman, Senior Researcher with the SIPRI Arms and Military Expenditure Programme.
"Russia, France and Germany dramatically increased their arms sales to Egypt in the past five years."
Asia and Oceania remains the largest importer region
States in Asia and Oceania received 40% of global arms imports in 2014–18, but there was a decrease of 6.7% compared with 2009–13. The top five arms importers in the region were India, Australia, China, South Korea and Viet Nam.

Australia became the world’s fourth largest arms importer in 2014–18 after its arms imports increased by 37% compared with 2009–13. Indian arms imports decreased by 24% between 2009–13 and 2014–18. Russia accounted for 58% of India’s arms imports in 2014–18. Chinese arms imports decreased, but it was still the world’s sixth largest arms importer in 2014–18.
‘India has ordered a large number of major arms from foreign suppliers; however, deliveries are severely delayed in many cases,’ says Siemon T. Wezeman, Senior Researcher with the SIPRI Arms and Military Expenditure Programme. ‘In contrast, Chinese arms imports decreased because China has been more successful in designing and producing its own modern weaponry.’
Other notable developments:
- Between 2009–13 and 2014–18 arms imports decreased by states in the Americas (–36%), in Europe (–13%), and in Africa (–6.5%).
- Algeria accounted for 56% of African imports of major arms in 2014–18. Most other states in Africa import very few major arms.
- The top five arms importers in sub-Saharan Africa were Nigeria, Angola, Sudan, Cameroon and Senegal. Together, they accounted for 56% of arms imports to the subregion.
- Between 2009–13 and 2014–18 British arms exports increased by 5.9%. In 2014–18 a total of 59% of British arms exports went to the Middle East, the vast bulk of which was made up of deliveries of combat aircraft to Saudi Arabia and Oman.
- Venezuelan arms imports fell by 83% between 2009–13 and 2014–18.
- China delivered major arms to 53 countries in 2014–18, compared with 41 in 2009–13 and 32 in 2004–2008. Pakistan was the main recipient (37%) in 2014–18, as it has been for all five-year periods since 1991.
Trends in International Arms Transfers, 2018, Pieter D. Wezeman, Aude Fleurant, Alexandra Kuimova, Nan Tian and Simeon T. Wezeman, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Resilience, Peace and SecuritySee all
Lisa Satolli
April 18, 2024
Kate Whiting
April 4, 2024
Spencer Feingold
March 22, 2024
Weekend reads: Our digital selves, sand motors, global trade's choke points, and humanitarian relief
Gayle Markovitz
March 15, 2024
Kalkidan Lakew Yihun
March 11, 2024
Liam Coleman
March 7, 2024






